
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
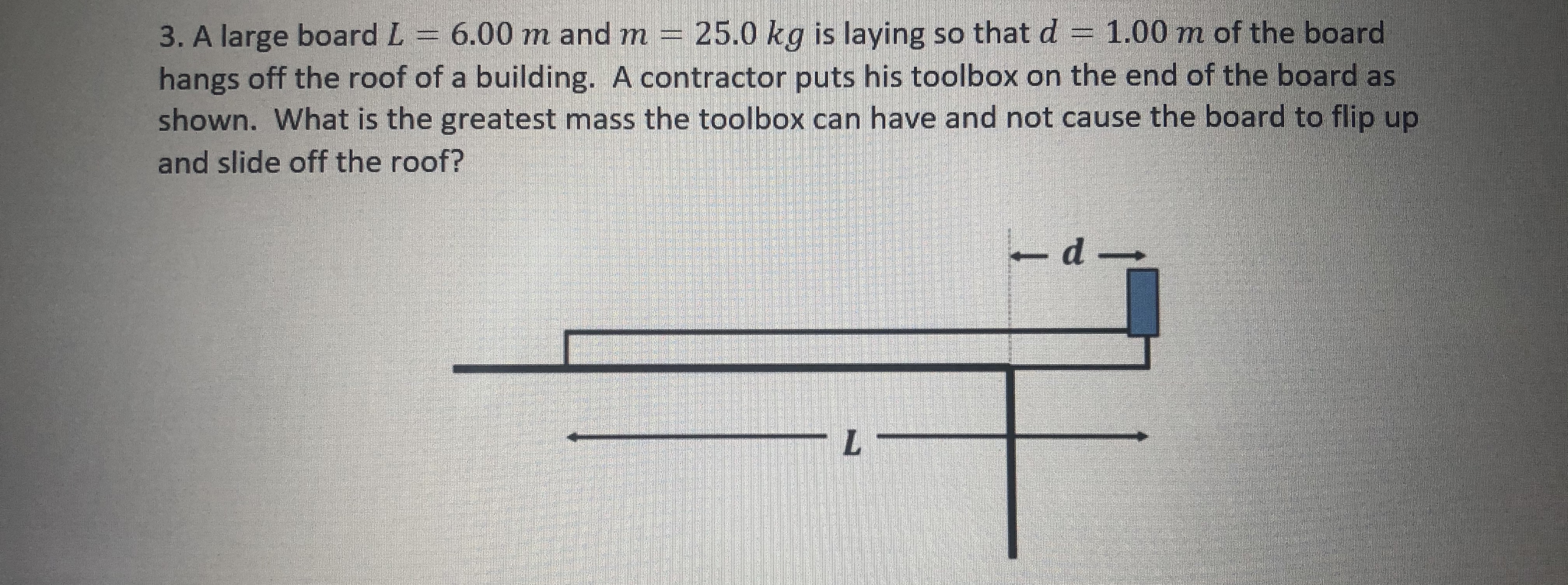
Transcribed Image Text:3. A large board L 6.00 m and m 25.0 kg is laying so that d = 1.00 m of the board
hangs off the roof of a building. A contractor puts his toolbox on the end of the board as
shown. What is the greatest mass the toolbox can have and not cause the board to flip up
and slide off the roof?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A 3.0 m long ladder, as shown in the diagram, leans against a frictionless wall. The coefficient of static friction between the ladder and the floor is 0.349. What is the minimum angle (in degrees) the ladder can make with the floor without slipping?arrow_forward7. What is the tension in each cable for the equilibrium configuration shown below? Cable A has a -x component, and positive y and z components, cable B is in the +x direction, and cable C has negative x and y components and a +z component. The 1300 N force is acting in the -z direction. +z C 2.0 m A 1.0 m 3.0 m 2.0 m 1.0 m 4.0 m Question #7 B +y +x 1300 N 8. By how much do the two springs stretch in the equilibrium configuration below in order to support the 25 kg mass? Each spring has an unstretched length of 2.2 m and a spring constant of 250 N/m. Spring A is exerting a force in the -y direction. Spring B is exerting a force in the -x direction.arrow_forwardA 200 N sign hangs from the middle of a cable between two buildings. The ends of each cable are attached to each building at the same height. The cable cannot exceed 1500 N without breaking. Find the minimum angle that the cable can make from the horizontal.arrow_forward
- 3. Two parents are doing some home improvement and their baby falls asleep on a board they are moving (parents of the year). The board is 3.80 m long and the baby is 0.45 m from one end of the board. The parents are holding the board from either edge. The board has a mass of 3.1 kg and the baby has a mass of 10.2 kg. Draw a free-body diagram and label each force and distances. Also choose and mark a pivot point for your board on the drawing. а. b. Write out E F and Ei for your diagram. Don't solve yet. For each of the torques you wrote down in part b, use the right-hand rule to say whether the direction of torque is into the page or out of the page. с.arrow_forwardthis is solution true or falsearrow_forwardQUESTION 11 A uniform, 5.0-m-long, 30-kg plank is suspended from a high ceiling by two, uniform, massless, vertical cables. A 70-kg painter is standing 1.5 m from the cable at the right end of the plank. What is the force of the cable on the plank at the right end? 1.5 m 5.0 m а. 117 N b. 225 N С. 453 N d. 628 N е. 784 Narrow_forward
- The figure shows a 1280 kg car that has slipped over the edge of an embankment. People are trying to hold the car in place by pulling on a horizontal rope. The car's bottom is pivoted on the edge of the embankment, and its center of mass lies farther back, as shown. 2,4m 1,8m 3 If the car makes a 34 degree angle with the horizontal, what force must the people apply to hold it in place? T=_Narrow_forwardA monkey of mass m = 10.0 kg is holding on to two vines each of length l = 3.00 m. The vines form an angle with the horizontal of 40.0 degrees (see figure). The monkey is not moving and the vines are considered massless and not stretchable. Determine the magnitude of the tension in each vine. d. Now the monkey moves up by clinging up the two vines, causing their angle with the horizontal to become smaller. If each vine breaks at a tension larger than T = 100 N, what is the smallest angel the vines can have with the horizontal?arrow_forward4. A wooden board of mass M and length L is hung from the ceiling by two massless wires attached to its two ends. A block of mass m is placed on the board. The two wires are of the same length. (a) the two wires is equal to each other? (b) along the board? (c) other. The thick wire can just sustain the maximum tension in part (b) while the thin wire can only sustain half of it. What is the requirement on the position of the block to avoid breaking the wires? Where is the block placed if it is known that the tension in What is the minimum and maximum of tension in the wires as we move the block Now assume M = 10 kg, m = 15 kg, and that one of the wires is thinner than thearrow_forward
- A hungry bear weighing 700 N walks out on a beam in an attempt to retrieve a basket of goodies hanging at the end of the beam (Fig. P8.22). The beam is uniform, weighs 200 N, and is 6.00 m long, and it is supported by a wire at an angle of 0 = 60.0°. The basket weighs 80.0 N. (a) Draw a force diagram for the beam. (b) When the bear is at x = 1.00 m, find the tension in the wire supporting the beam and the components of the force exerted by the wall on the left end of the beam. (c) If the wire can withstand a maximum tension of 900 N, what is the maximum distance the bear can walk before the wire breaks?arrow_forwardQ13. A 5 meter, 200N-long ladder rests against a wall. The ladders center of mass is 3.0 meters up the ladder. The coefficient of friction on the ground is 0.30. How far along the ladder can a 75-kg person climb before it slips? The angle between the ladder and ground is 56 degrees. (2.0 m)arrow_forwardIn exercise physiology studies, it is sometimes important to determine the location of a person's center of mass. This determination can be done with the arrangement shown in the figure below. A light plank rests on two scales, which read F, = 395 N and F, gi = 340 N. A distance of 1.65 m separates the scales. How far from the woman's feet is her center of mass? g2 1.65 m F 18. F 82arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON