
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
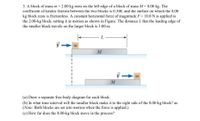
Transcribed Image Text:3. A block of mass m = 2.00 kg rests on the left edge of a block of mass M = 8.00 kg. The
coefficient of kinetic friction between the two blocks is 0.300, and the surface on which the 8.00
kg block rests is frictionless. A constant horizontal force of magnitude F = 10.0 N is applied to
the 2.00-kg block, setting it in motion as shown in Figure. The distance L that the leading edge of
the smaller block travels on the larger block is 3.00 m.
m
(a) Draw a separate free-body diagram for each block.
(b) In what time interval will the smaller block make it to the right side of the 8.00-kg block? as
(Note: Both blocks are set into motion when the force is applied.)
(c) How far does the 8.00-kg block move in the process?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 11 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 4.6-kg block is pushed 2.3 m up a vertical wall with constant speed by a constant force of magnitude F applied at an angle of ? = 30° with the horizontal, as shown in the figure below. If the coefficient of kinetic friction between block and wall is 0.30, determine the following. A figure, drawn from a side view, shows the right side of a rectangular block pushed up against a rough, vertical wall. A force vector F acts on the block and is represented by a diagonal rrow pointing up and to the right, toward the center of the block's left side. The arrow forms an angle ? with the horizontal. (a) the work done by F J(b) the work done by the force of gravity J(c) the work done by the normal force between block and wall J(d) By how much does the gravitational potential energy increase during the block's motion? Jarrow_forwardQ2: The mass center of the rear-engine 1500- kg car is at G. Determine the normal forces NA and Ng exerted by the road on the front and rear pairs of tires for the conditions of (a) being stationary and (b) braking from a forward velocity v with all wheels locked. The coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.90 at all tire/road interfaces. Ans.: (a) NA= (b) NA = 5886 N, NB = 8775N, NB = 8829 N 5940 N 600 mm B 1650 mm 1100 mmarrow_forwardA 2.2-kg sphere S is being moved in a vertical plane by a robotic arm. When the angle is 36°, the angular velocity of the arm about a horizontal axis through O is 45 deg/s clockwise and its angular acceleration is 176 deg/s² counterclockwise. In addition, the hydraulic element is being shortened at the constant rate of 550 mm/s. Determine the necessary minimum gripping force P if the coefficient of static friction between the sphere and the gripping surfaces is 0.58. Compare P with the minimum gripping force P, required to hold the sphere in static equilibrium in the 36° position. 1.0 m $ Answers: P= Ps= i i N Narrow_forward
- Problem 2 Determine the magnitude of W so that the 200-lb body will have an acceleration up the plane of 4.025 ft/s² . Coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.20. 200 lb 30° W lbarrow_forwardThe 250-lb pipe is being towed behind a truck, as shown in the figure. If θ = 25° and the coefficient of friction of the pipe with the ground is μk = 0.25, determine: a) the tension in the cable b) the acceleration of the truckarrow_forward7arrow_forward
- NEED ASAParrow_forwardA 35-kg child rides on a 10-kg bicycle with 500-mmdiameter wheels. Determine the horizontal force necessary to push the child and bicycle On a level sidewalk.Neglect all friction except rolling resistance.arrow_forwardQ4.) The 12 kg block A and 10 kg block B are pinned to a rod having negligible mass and resting on horizontal surfaces. A horizontal force P is applied to the rod at end C increasing gradually from zero until motion first begins. a) If the coefficient of static friction between both blocks and each surface is μ = 0.45, determine the value for P at which point motion first begins and describe the motion that occurs in a few brief words. b) If the coefficient of static friction between both blocks and each surface is μ = 0.6, determine the value for P at which point motion first begins and describe the motion that occurs in a few brief words. (Hint: Consider drawing the system as one FBD for this analysis and treat each block as a particle with negligible dimensions) 100 mm 200 mm с Bo 10 kg 25° A 12 kg 12 kgarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY