
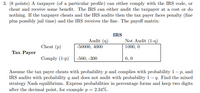
(8 points) A taxpayer (of a particular profile) can either comply with the IRS code, or
cheat and receive some benefit. The IRS can either audit the taxpayer at a cost or do
nothing. If the taxpayer cheats and the IRS audits then the tax payer faces penalty (fine
plus possibly jail time) and the IRS receives the fine. The payoff matrix:
IRS
Audit (q) Not Audit (1-q)
Cheat (p) -50000, 4000 1000, 0
Tax Payer
Comply (1-p) -500, -300 0, 0
Assume the tax payer cheats with probability p and complies with probability 1 − p, and
IRS audits with probability q and does not audit with probability 1 − q. Find the mixed
strategy Nash equilibrium. Express probabilities in percentage forms and keep two digits
after the decimal point, for example p = 2.34%.
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

- What P(s1) would the decision-maker be indifferent between the "buy" and "make" decisions, all other data input remaining the same?arrow_forwardPlease answer all questions. Note:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism.Answer completely.You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forwardNote:- Do not provide handwritten solution. Maintain accuracy and quality in your answer. Take care of plagiarism. Answer completely. You will get up vote for sure.arrow_forward
- 8arrow_forwardCan you help me with this please?arrow_forward1. Individual Problems 17-1 Malaysia You're the manager of global opportunities for a U.S. manufacturer that is considering expanding sales into Asia. Your market research has identified the market potential in Malaysia, the Philippines, and Singapore as described in the following table: Success Level Big Mediocre Failure Malaysia Probability 0.7 0.1 0.2 Units 1,300,000 416,000 0 Philippines Probability 0.2 0.3 0.5 Units 600,000 360,000 0 Singapore Probability 0.4 0.3 0.3 Units 1,500,000 750,000 0 The product sells for $20, and each unit has a constant marginal cost of $16. Assume that the (fixed) cost of entering the market (regardless of which market you select) is $500,000. In the following table, enter the expected number of units sold, and the expected profit, from entering each market. Market Expected Number of Units Sold Expected Profit Malaysia Philippines Singapore…arrow_forward
- 25 Y 20 15 10 5 B3, 0 B2 B1 0 12 13 C 13 b 12 5 05. Point (c) compared to point (b) 10 GD 15 (a) represents a higher level of utility. (b) represents the same level of utility, but is less expensive. (c) represents a higher level of utility and is less expensive. (d) represents a lower level of utility but is less expensive. (e) none of the above. 20 L 11 Xarrow_forwardGovernments often require people to obtain insurance; for example, all drivers are required to carry auto insurance to cover damages to others in the event of a crash. Homeowners are often required by banks to carry insurance on their home. (a) Why do these requirements exist? (b) Would they be necessary if people truly recognized the risk they faced? (c) One characteristic of an overconfident person is that she is continually surprised when what she thought was unlikely orarrow_forwardQuestion a Full explain this question and text typing work only We should answer our question within 2 hours takes more time then we will reduce Rating Dont ignore this line . .arrow_forward

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education





