
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
15-42. A toboggan having a mass of 10 kg starts from rest at A and carries a girl and boy having a mass of 40 kg and 45 kg, respectively. When the toboggan reaches the bottom of the slope at B, the boy is pushed off from the back with a horizontal velocity of Vb/t = 2 m/s, measured relative to the toboggan. Determine the velocity of the toboggan afterwards. Neglect friction in the calculation
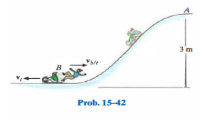
Transcribed Image Text:3 m
B
Prob. 15-42
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 2. Initially the 5-kg block is moving with a constant speed of 2 m/s around the circular path centered at 0 on the smooth horizontal plane. If a constant tangential force F = 5 N is applied to the block, determine its speed when t = 3 s. Neglect the size of the block. 1.5 m F = 5 N 2 m/sarrow_forwardThe block has a mass of 40 kg and rests on the surface of the cart having a mass of 78 kg If the spring which is attached to the cart and not the block is compressed 0.2 m and the system is released from rest, determine the speed of the block with respect to the cart after the spring becomes undeformed. Neglect the mass of the wheels and the spring in the calculation. Also neglect friction. Take k = 310 N/marrow_forwardThe two flat cars A and B each have a mass of 80kg. If the man C has a mass of 70kg and jumps from A with a horizontal relative velocity of vC/A= 2 m/s and lands on B, determine the velocity of each car after the jump. Neglect the effect of rolling resistance.arrow_forward
- The motor, M, pulls on the cable with a force F = (101² + 300)N, where t is in seconds. If the 100 kg crate is originally at rest at 1 = 0, determine its speed when t = 4 s. Hint: First find the time needed to begin lifting the crate.arrow_forwardQ17. As shown in the image below, the 0.7-kg ball strikes the rough ground and rebounds. The directions of its velocities before and after the strike are shown. If the speeds are v₁ = 27 m/s and v₂ = 12 m/s, determine the magnitude of the impulse (in N.s) the ground exerts on the ball. Assume that the ball does not slip when it strikes the ground, and neglect the size of the ball and the impulse produced by the weight of the ball. Please pay attention: the numbers may change since they are randomized. Your answer must include 2 places after the decimal point. V₁ Your Answer: 45° Answer 30° 02arrow_forwardThe 64.4-lb slider moves in the vertical plane on a smooth rail. The spring with k = 800 lb/ft is unstretched with the slider at point B. If the slider is released from rest at point A, what is the speed at point C? The slider can be approximated as a particle. 인 it woll 3 ft C abert --www- A B 3 ftarrow_forward
- A toboggan having a mass of 12 kg starts from rest at A and carries a girl and boy having a mass of 40 kg and 45 kg, respectively. When the toboggan reaches the bottom of the slope at B, the boy is pushed off from the back with a horizontal velocity of vỏ/t = 2 m/s, measured relative to the toboggan. Suppose that h = 3.2 m. Neglect friction in the calculation. (Figure 1) Figure B vbil A h Part A Determine the velocity of the toboggan afterwards. Express your answer to three significant figures and include the appropriate units. Vt = Submit Value Provide Feedback Request Answer Units ?arrow_forward5. The 8-kg smooth collar has a speed of 5 m/s when it is at s = 0. Determine the maximum distance s it travels before it stops momentarily. The spring has an unstretched length of 2 m. -1.5 m- -3 m/s k = 100 N/marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY