
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Gate AB retains water as shown in the figure. The gate is supported every 2 m (perpendicular to the plane of view) by member BC, which is attached to a 2000 kg mass at point C. What minimum static coefficient of friction μs, along the contact surface between the mass and its base, is needed for the gatestructure to be in equilibrium? There are pins at points A, B, andC.
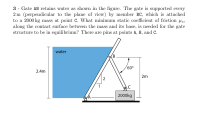
Transcribed Image Text:3 - Gate AB retains water as shown in the figure. The gate is supported every
2 m (perpendicular to the plane of view) by member BC, which is attached
to a 2000 kg mass at point C. What minimum static coefficient of friction us,
along the contact surface between the mass and its base, is needed for the gate
structure to be in equilibrium? There are pins at points A, B, and C.
water
(B
60°
2.4m
2m
2
1
2000kg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the reactions at A and B for the steel bar and loading shown in figurearrow_forward1. The member is loaded as shown. The diameter of the member is 32 mm. 1) Calculate all internal loadings on the cross section through the point A. 2) Calculate the stress at point A due to each internal loading. 0.4 m A Rigid Wall 1000 N 300 Nm 2000 Narrow_forwardPlease provide solution for this questionarrow_forward
- A cross-section is subjected to a maximum shear of V=160 kN (see figure): Determine the centroid of the cross-section. Calculate the moment of inertia (I) of the cross-section. Determine the shear stress at point A in the cross-section.arrow_forwardThe solid 1.05-in.-diameter rod is subjected to a uniform axial distributed loading along its length of w = 800 lb/ft. Two concentrated loads also act on the rod: P= 2300 lb and Q = 1400 lb. Assume a = 12 in. and b = 24 in. Determine the normal stress in the rod at the following locations: (a) x = 8 in. (b) x = 24 in. → → -→ P B a Answer: Ox=8in. = psi Ox=24in. = psiarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning