
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
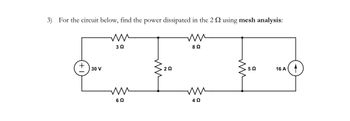
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem Statement:**
3) For the circuit below, find the power dissipated in the \(2 \, \Omega\) resistor using mesh analysis:
**Circuit Description:**
The circuit consists of the following components arranged in a closed loop:
- A voltage source of \(30 \, \text{V}\) connected in series with a \(6 \, \Omega\) resistor on the left side.
- Moving clockwise, a \(3 \, \Omega\) resistor follows the \(30 \, \text{V}\) voltage source.
- Adjacent to the \(3 \, \Omega\) resistor, there is a \(2 \, \Omega\) resistor connected horizontally.
- Parallel to the \(2 \, \Omega\) resistor is an \(8 \, \Omega\) resistor continuing around the loop.
- Below the \(8 \, \Omega\) resistor is a \(4 \, \Omega\) resistor connected horizontally parallel to the \(6 \, \Omega\) resistor.
- A \(5 \, \Omega\) resistor is connected vertically between the parallel branches of the \(2 \, \Omega\) and \(4 \, \Omega\) resistors.
- On the right side of the circuit, a \(16 \, \text{A}\) current source completes the loop, placed parallel to the \(5 \, \Omega\) resistor.
**Objective:**
Apply mesh analysis to determine the power dissipated in the \(2 \, \Omega\) resistor.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- solve for v, and i, in the circuit. (Use nodal analysis)arrow_forward2. For the circuit below, assume the 10Ω is the load: A. Find the Thevenin equivalent resistance and voltage. B. Draw the Thevenin equivalent circuit. C. Use your result on part B to find the voltage vx.arrow_forwardWhich of the sources require a supermesh for mesh analysis? b) 2mA d) 3V a) 1mA c) 1Varrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,