
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
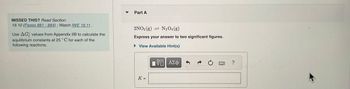
Transcribed Image Text:MISSED THIS? Read Section
19.10 (Pages 881 884); Watch IWE 19.11.
Use AG values from Appendix IIB to calculate the
equilibrium constants at 25°C for each of the
following reactions.
Part A
2NO2 (g)
N2O4 (g)
Express your answer to two significant figures.
► View Available Hint(s)
K =
πΨΕΙ ΑΣΦ
?
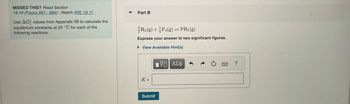
Transcribed Image Text:MISSED THIS? Read Section
19.10 (Pages 881-884); Watch IWE 19.11.
Use AG values from Appendix IIB to calculate the
equilibrium constants at 25°C for each of the
following reactions.
Part B
³H₂(g) + ½P4(g) = PH3(g)
Express your answer to two significant figures.
► View Available Hint(s)
K=
Submit
VE ΑΣΦ
Ć
3 ?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the reaction for the formation of aluminum oxide from aluminum and oxygen. 4 Al(s) + 3 0,(g) → 2 Al,O,(s) ΔΗ Express the enthalpy of the following reaction, AH2, in terms of AH1. 2 Al,0,(s) → 4 Al(s) + 3 0,(g) ΔΗ AH2 = Express the enthalpy of the following reaction, AH3, in terms of AH1. 12 Al(s) + 9 O,(g) → 6 Al, O3(s) ΔΗ | AH3 = S A étv MacBook Air 80 000 000 DII DD F3 F4 F5 F6 F7 FB F9 F10 F11 F12arrow_forwardDescribe the process of sublimation in terms of heat energy, relating what happens to the behavior of matter. Answer in complete sentences. H I ||| Normal E = AA Enter your answer here ||' _||| = BIUS √x X₂ 2 Ixarrow_forwardGiven these reactions, where X represents a generic metal or metalloid 1) H, (g) + 0,(g) → H,0(g) AH1 = -241.8 kJ 2) X(s) + 2 Cl,(g) → XCl,(s) AH2 = +475.9 kJ 3) H,(g) + CL,(g) HCl(g) АНз 3 —92.3 kJ → 4) X(s) + O,(g) –→ XO,(s) AH4 = -748.7 kJ 5) Н, О(2) — н,00) AH5 = -44.0 kJ what is the enthalpy, AH, for this reaction? XCI, (8) + 2H,О() — ХО,(8) + 4 HCI(g)arrow_forward
- Please don't provide handwritten solution ....arrow_forward(b) What is the first law of thermodynamic? Define the Hess law. Given the following data; 2CIF(g) + 0,(g) CI,0(g) + F,O(g) AH = 167.4 kJ AH = 341.4 kJ SH = -43,4 kJ 2CIF,(g) + 20,(g) → CĻ0(g) + 3F,O(g) 2F,(2) + O(8) → 2F,O(g) calculate AH for the reaction CIF(g) + F(8) CIF,(g)arrow_forwardWhich molecules are enantiomers? Which molecules are the same? (A). H Brarrow_forward
- Order these chemical species by increasing pH of an 0.1 M aqueous solution of each. That is, imagine making an 0.1 M solution of each species. Select1 next to the species that makes the solution with the lowest pH. Select 2 next to the species that makes the solution with the next higher pH, and so on. Notice that some of the rankings have been filled in for you already. Also notice that water is on the list. For that particular case, just compare the pH of pure water to the pH of the other solutions. Note for advanced students: for all charged species, you may assume the necessary counterions act as neither acids nor bases. relative pH of 0.1 M aqueous solution species H20 4 H,PO4 HNO, (Choose one) NO2 7 OH (Choose one) HF (Choose one) ▼arrow_forwardUsing the information below, calculate AH of NH3(g) + HCI(g) NH,CI(s). N, (8) + H, (8) NH,(g) AH = -46.19 kJ/mol > H, (g) + Cl,(8) → HCl(g) AH = -92.30 kJ/mol N, (8) + 2 H, (g) +Cl,(g) NH,Cl(s) AH = –314.4 kJ/mol • Your answer should have four significant figures. Provide your answer below: kJ/molarrow_forwardClassify the substances below as reactants or products and state their state of 2NaHCO3 (s) → Na,CO3 (s) + H20 (1) + CO2 (g) matter:arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY