
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
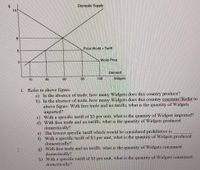
Transcribed Image Text:Domestic Supply
2$
14
8.
Price-World + Tariff
World Price
3
Demand
10
40
60
80
100
Widgets
1. Refer to above figure.
a) In the absence of trade, how many Widgets does this country produce?
b) In the absence of trade, how many Widgets does this country consume?Refer to
above figure. With free trade and no tariffs, what is the quantity of Widgets
imported?
c) With a specific tariff of $3 per unit, what is the quantity of Widgets imported?
d) With free trade and no tariffs, what is the quantity of Widgets produced
domestically?
e) The lowest specific tariff which would be considered prohibitive is
f) With a specific tariff of $3 per unit, what is the quantity of Widgets produced
domestically?
g) With free trade and no tariffs, what is the quantity of Widgets consumed
domestically?
h) With a specific tariff of $3 per unit, what is the quantity of Widgets consumed
domestically?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 2. The impact of a tariff Consider a hypothetical example of trade in aluminum between the United States and China. For simplicity, assume that China is the only source of U.S. aluminum imports. The following graph shows the U.S. market for aluminum. Note that in the absence of any trade, the market price for aluminum in the United States is $500 per tonne, and the equilibrium quantity is 250 million tonnes per month. Use the green area (triangle symbol) to show U.S. consumer surplus under free trade with China, and use the purple area (diamond symbol) to show U.S. producer surplus under free trade with China. 1000 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 900 Consumer Surplus 800 700 Producer Surplus 600 500 400 Free Trade Price 300 200 100 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 50 100 150 QUANTITY OF ALUMINUM (Millions of tonnes per month) PRICE (Dollars per tonne)arrow_forward▪Figure: The Home and World Markets ▪ The supplied graph shows the case for a tariff imposed by a large country. Home market World market Price I $36 $30 $26 SO 20 40 80 100 Quantity Price C) $160; $120 'D) $120; $120 40 80 X + 1 Imports Q1. (Figure: The Home and World Markets) The terms-of-trade gain is deadweight loss is 'A) $120; $160 'B) $160; $160 and the ↑. 1. ↑. ↑.arrow_forwardQuantify the effects of a country’s tariff on sugar Situation with import tariff Estimated situation without tariff World price $0.10per pound $0.10per pound Tariff $0.02per pound 0 Domestic price $0.12per pound $0.10per pound Domestic consumption (billions of pounds per year) 20 22 Domestic production (billions of pounds per year) 8 6 Imports (billions of pounds per year) 12 16 Calculate the following measures:• The domestic consumers’ gain from removing the tariff. • The domestic producers’ loss from removing the tariff. • The government tariff revenue loss.• The net effect on national well-being.arrow_forward
- Figure 9-6 PRICE 219 12 Domestic Supply 11 Domestic Demand 10 9 B E World Price +Tariff World Price 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 QUANTITY Refer to Figure 9-6. The area C+D+E+F represents O the deadweight loss of the tariff minus government revenue raised by the tariff. O the decrease in total surplus caused by the tariff. O the deadweight loss of the tariff plus government revenue raised by the tariff. O the decrease in consumer surplus caused by the tariff.arrow_forward4. Effects of a tariff on international trade The following graph shows the domestic supply of and demand for wheat in Bangladesh. The world price (Pw) of wheat is $270 per bushel and is represented by the horizontal black line. Throughout the question, assume that the amount demanded by any one country does not affect the world price of wheat and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in wheat. Also, assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place. 540 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 510 480 450 420 390 360 330 300 270 240 PRICE (Dollars per bushel) Pw 0 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 QUANTITY (Bushels of wheat) 400 bushels of wheat. If Bangladesh is open to international trade in wheat without any restrictions, it will import Suppose the Bangladeshi government wants to reduce imports to exactly 200 bushels of wheat to help domestic producers. A…arrow_forwardQuestion 2 Full explain this questionarrow_forward
- Using a domestic-market demand- and supply-curve graph, a. show the impact of tariff on a small country's import price, domestic demand, domestic supply, import quantity, consumer surplus, producer surplus, government revenue, and total welfare; b. Is the country unambiguously worse off as a result of the tariff? c. In the same graph, show how to achieve the same import quantity with an import quota; d. When would the tariff and the import quota lead to the same amount of welfare change? e. How would the answers to (a) and (b) change for a large country?arrow_forwardFigure 7-2 Price (dollars per pound) $3.00 2.50 1.75 0.50 12 18 26 38 45 U.S. Supply U.S. Demand Quantity of coffee (millions of pounds) Suppose the U.S. government imposes a $0.75 per pound tariff on coffee imports. Figure 7-2 shows the impact of this tariff. Refer to Figure 7-2. Without the tariff in place, the United States consumes 12 million pounds of coffee. Pw+tariff World price (P 26 million pounds of coffee. 33 million pounds of coffee. 45 million pounds of coffee.arrow_forward4. Effects of a tariff on international trade The following graph shows the domestic supply of and demand for soybeans in Zambia. The world price (Pw) of soybeans is $520 per ton and is represented by the horizontal black line. Throughout the question, assume that the amount demanded by any one country does not affect the world price of soybeans and that there are no transportation or transaction costs associated with international trade in soybeans. Also, assume that domestic suppliers will satisfy domestic demand as much as possible before any exporting or importing takes place. 920 Domestic Demand Domestic Supply 870 820 770 720 670 620 570 520 470 420 80 100 120 140 QUANTITY (Tons of soybeans) 20 40 60 160 180 200 If Zambia is open to international trade in soybeans without any restrictions, it will import tons of soybeans. Suppose the Zambian government wants to reduce imports to exactly 40 tons of soybeans to help domestic producers. A tariff of S per ton will achieve this. A…arrow_forward
- Suppose that the world price of baseball caps is €1 and there are no import restrictions on this product. Assume that Spanish consumers are indifferent between domestic and imported baseball caps. a. What quantity of baseball caps will domestic suppliers supply to domestic consumers ?__________thousandsarrow_forwardFigure 9-2 Price (dollars per pound) $1.00 0.60 0 G C ان H A D 1 9 15 9 million pounds of rice. O 15 million pounds of rice. B 31 million pounds of rice. E 42 million pounds of rice. J US Supply 31 F K 42 Suppose the U.S. government imposes a $0.40 per pound tariff on rice imports. Figure 9-2 shows the impact of this tariff. Pw World price (Pw) Refer to Figure 9-2. Without the tariff in place, the United States produces + tariff US Demand Quantity of rice (millions of pounds)arrow_forward1. Andorra is a small country, incapable of affecting world prices. It imports peanuts at the world price of 10 cents per sack. Andorra's demand for peanuts is given by: D = 400– 10P. Andorra's supply curve for peanuts is: S = -20 + 5P. Determine the equilibrium under free trade. a) Calculate and show in a diagram the following effects of a quota that limits the import of peanuts to 60 sacks. · The increase in the domestic price. · The quota revenue. · The loss due to production distortion. · The loss due to consumption distortion. b) Could the Government of Andorra have achieved the same trade result using a tariff?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education