
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
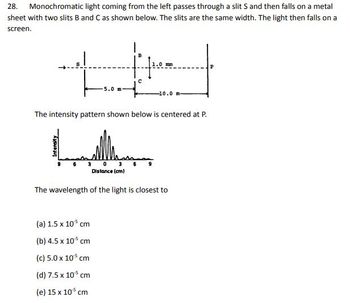
Transcribed Image Text:28. Monochromatic light coming from the left passes through a slit S and then falls on a metal
sheet with two slits B and C as shown below. The slits are the same width. The light then falls on a
screen.
5.0 m
с
-10.0
The intensity pattern shown below is centered at P.
0 3
Distance (cm)
The wavelength of the light is closest to
(a) 1.5 x 105 cm
(b) 4.5 x 105 cm
(c) 5.0 x 105 cm
(d) 7.5 x 105 cm
(e) 15 x 105 cm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Monochromatic light falls on two very narrow slits 0.046 mm apart. Successive fringes on a screen 6.50 m away are 8.2 cm apart near the center of the pattern. A) Determine the wavelength of the light. B) Determine the frequency of the light.arrow_forward4. What is the wavelength of light falling on double slits separated by 2.00 µm if the second- order maximum is at an angle of 60.0°? 5. Calculate the distance between two adjacent fringes for 633-nm light falling on double slits separated by 0.0800 mm, located 3.00 m from a screen.arrow_forward2. If the light is replaced by another light with two wavelengths 700nm and 800nm. Is there any chance of overlapping of bright fringe by wavelength1 with bright fringe of wavelength of 2.arrow_forward
- 6. Structures on a hummingbird feather act like a diffraction grating having 8000 lines per centimeter. What is the angle of the first-order maximum for 488-nm light? 2 7. When red light illuminates a grating with 7000 lines per centimeter, its second maximum is at 62.4°. What is the wavelength of this light?arrow_forward6. A beam of light traveling in air has a wavelength of 475 nm. If the light illuminates a diffraction grating with 3000 lines/cm, what is the angle of the second-order bright spot produced? f19 0 oof19arrow_forwardWhen polychromatic visible light shines through a diffraction grating, the colors seen closest to the central maximum will: A. be visible as the lowest wavelength in the mixture B. be visible as the highest wavelength in the mixture C. be a mixture of the wavelengths present D. Always be whitearrow_forward
- 5. Draw the variation of the mean light intensity (l) with respect to the angle of diffraction (teta) if i is due to interference of light of wavelength (lamda) using 2 slits. It is known that each slit has a width of a(- 2 lamda) and the distance between the two slits is d(- 4 lamda).arrow_forward3. In a double slit experiment, the distance between the slits is d=1 mm. A screen is situated at a distance of 2.5 m from the slits. Point P is at a distance of 25 cm from O', as in Figure. O' is the orthogonal projection of the center between the slits (0) on the screen. Monochromatic light with frequency v= 550 THz is used in this experiment. (a) Calculate the intensity of light at point P. (b) Calculate the angle ZP00'. (c) Calculate the location of the first three maxima with respect to point O'. (d) Calculate the location of the first three minima with respect to point O'. BONUS: You now consider that each slit has width a =0.05 mm. Calculate the intensity of light at point P. P.arrow_forward10. Please refer to the Figure which shows the pattern of interference fringes for light of wavelength 609 nm passing through two narrow slits, projected onto a screen a distance of 2.27 m away. The distance on the screen between the centers of two adjacent bright fringes is 1.42 cm. What is the distance between the two slits? 7.79E-05 m 9.74E-05 m 1.75E-04 m 1.27E-04 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON