
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
![**Problem 27:** A radar signal took 2.7 seconds to travel to the moon and back. How far away was the moon at that time?
To determine the distance between the Earth and the moon, we can use the speed of light, which is approximately \(299,792,458\) meters per second. The total travel time for the radar signal is 2.7 seconds.
The formula to calculate the distance \(d\) is:
\[ d = \frac{{\text{speed of light} \times \text{time}}}{2} \]
Substituting the known values:
\[ d = \frac{{299,792,458 \, \text{m/s} \times 2.7 \, \text{s}}}{2} \]
By performing the calculation, you arrive at the approximate distance from Earth to the moon at that time.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/d32c0099-d35b-45af-b7af-24c06e9e82b9/dfb5470c-6484-4d6a-8c13-e6106762eb93/mxc615fe_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:**Problem 27:** A radar signal took 2.7 seconds to travel to the moon and back. How far away was the moon at that time?
To determine the distance between the Earth and the moon, we can use the speed of light, which is approximately \(299,792,458\) meters per second. The total travel time for the radar signal is 2.7 seconds.
The formula to calculate the distance \(d\) is:
\[ d = \frac{{\text{speed of light} \times \text{time}}}{2} \]
Substituting the known values:
\[ d = \frac{{299,792,458 \, \text{m/s} \times 2.7 \, \text{s}}}{2} \]
By performing the calculation, you arrive at the approximate distance from Earth to the moon at that time.
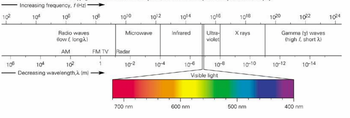
Transcribed Image Text:The image demonstrates the electromagnetic spectrum, showcasing the relationship between frequency (f) and wavelength (λ).
**Top Axis (Frequency):**
- The axis shows the frequency in hertz (Hz), increasing from left to right.
- The frequency scale ranges from \(10^2\) Hz (low frequency) to \(10^{24}\) Hz (high frequency).
**Bottom Axis (Wavelength):**
- The axis depicts wavelength in meters (m), decreasing from left to right.
- The wavelength scale ranges from \(10^6\) m (long wavelength) to \(10^{-14}\) m (short wavelength).
**Regions of the Electromagnetic Spectrum:**
- **Radio Waves:** Located at the leftmost part, characterized by low frequency and long wavelength. Includes AM, FM, and TV waves.
- **Microwave:** Higher frequency and shorter wavelength than radio waves. Includes radar waves.
- **Infrared:** Positioned after microwaves with shorter wavelengths.
- **Visible Light:** Small segment in the middle, ranging from 700 nm (red) to 400 nm (violet).
- **Ultraviolet:** Follows visible light, having yet higher frequencies and shorter wavelengths.
- **X-rays:** Come after ultraviolet, with even more elevated frequencies.
- **Gamma (\(\gamma\)) Waves:** At the rightmost end, featuring the highest frequency and shortest wavelength, described as high f, short λ.
**Visible Light Spectrum:**
- An enlarged section shows the visible light spectrum in detail, indicating colors corresponding to wavelengths from 700 nm (red) to 400 nm (violet).
This diagram effectively illustrates how electromagnetic waves vary across different regions in terms of frequency and wavelength.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 1. Radio waves transmitted through space at 3 x10°m/s by the Voyager spacecraft have a wavelength of 0.133 m. What is their frequency? Frequency, f:arrow_forwardWhat is the frequency of infrared light of 1.0*10^-4 wavelength?arrow_forward15.) Because gamma rays have the highest frequency and carry the most energy, a. they are sometimes used to kill cancer cells b. they are widely used for communication over long distances c. they are very valuable for thermal imagingarrow_forward
- A local radio station broadcasts radio waves at 99.7 MHz. Unlike sound, radio waves can pass into outer space, because they are disturbances not in air molecules but in the e-m fields that exist even in the vacuum of space. It's energy traveling independent of matter. a. When that radio wave hits you, how many pulses (wave crests) of em radiation hit you per minute (60 seconds)? (reminder: M = 10 6) b. Radio waves move at the speed of light (c), how far apart is each wave crest (wavelength)? c. If we boosted the signal strength so that station could be heard on the moon, would either the wavelength or frequency change?arrow_forwardA high-altitude airplane is used to make observations a. at gamma-ray wavelengths. b. at X-ray wavelengths. c. in the ultraviolet. d. in the infrared.arrow_forwardWhat is the most amount of time (in minutes) for a signal from the Mars Rover to reach Earth? (This is when Mars and Earth are farthest apart at 401 million km.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON