Question
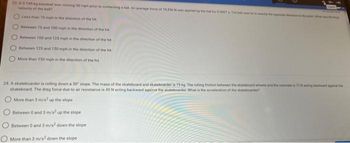
Transcribed Image Text:23. A 0 145 kg baseball was moving 90 mph prior to contacting a bat. An average force of 18.436 N was applied by the bat for 0.0007 The hell we
velocity of the ball?
Less than 75 mph in the direction of the hit
Between 75 and 100 mph in the direction of the hit
Between 100 and 125 mph in the direction of the hit
Between 125 and 150 mph in the direction of the hit
More than 150 mph in the direction of the hit
24. A skateboarder is rolling down a 30 slope. The mass of the skateboard and skateboarder is 75 kg. The rolling friction between the skateboard wheels and the concrete is 72N acting backward against the
skateboard. The drag force due to air resistance is 45 N acting backward against the skateboarder. What is the acceleration of the skateboarder
More than 3 m/s up the slope
Between 0 and 3 m/s² up the slope
Between 0 and 3 m/s² down the slope
More than 3 m/s2 down the slope
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 1. A 3 N baseball moving left toward the batter with a velocity of 15 m/s is struck with a bat which causes it to move in a reversed direction with a velocity of 30 m/s. Calculate the average force exerted on the ball if the bat is in contact with the ball for 0.01 s.arrow_forwardA golf club exerts an average horizontal force of 1000 N on a 0.045-kg golf ball that is initially at rest on the tee. The club is in contact with the ball for 1.8 ms. What is the speed of the golf ball just as it leaves the tee? A) 40 m/s B) 0.40 m/s c) 4.0 m/s 400 m/sarrow_forward1.) A car that weighs 4000 Ibs. (1814 kg), crashes into a wall. What is the impulsive force (F) if the car goes from 55 mph (88.5 km/h - 24.6 m/s) to 0 m/s in 0.3 sec? Force Units 2.) What if the same car, traveling at the same speed as before, had "crumple zones" (longer time to stop). When this car hits the wall, it takes 0.75 seconds to come to a rest. What is the new impulsive force (F) on the driver? Force - Units 3.) In a car collision, the driver's body must change speed from a high value to zero. This is true whether or not an airbag is used. How does an airbag reduce injuries? 4.) A baseball is pitched at 35 m/s is hit by a batter. After leaving the bat, the ball has a velocity of 50 m/s. The ball weighs 0.15 kg. The time elapsed during the collision was 0.0015 seconds. What was the force (F) exerted on the baseball? Hint: Watch your signs of the velocities, the direction changes. Force = Unitsarrow_forward
- answer both questions.. Q25.. only typingarrow_forwardH9arrow_forwardA 2500 kg truck traveling at 80 km/h collides with another car of mass 1000 kg traveling at 50 km/h in the same direction. The two cars stick together after the collision. Their speed immediatley after the collison is 1. 42.85 km/hr 2. 51.75 km/hr 3. 71.42 km/hr 97.77 km/hr nonearrow_forward
- Fx (N) 15 10- 5 0 0 1 Donal filanten, ing shy Pay 2 3 -x (m) A 537 g particle moving along the x-axis experiences the force shown in the diagram. The particle's velocity is 5.40 m/s at x = 0 m. What is its velocity (in m/s) at x = 1 m? Submit Answer Tries 0/10 What is its velocity (in m/s) at x = 2 m? Submit Answer Tries 0/10 What is its velocity (in m/s) at x = 3 m? Submit Answer Tries 0/10arrow_forwardA 2.0 kg object moving to the right with speed 0.50 m/s experiences the force is shown. What are the object's speed and direction after the force ends? * F. (N) 2 0. t (s) -2 - 0.50 m/s left At rest 0.50 m/s right 1.0 m/s right 2.0 m/s right 12arrow_forwardWhat is the average force on the ball of it is in contact with the club for 2.20ms?arrow_forward
- Physics A catcher in a baseball game stops a pitched ball originally moving at 49.0 m/s49.0 m/s in the positive direction at the moment it first comes in contact with the catcher’s glove. After contacting the glove, the ball travels an additional 10.5 cm10.5 cm before coming to a complete stop. The mass of the ball is 0.145 kg.0.145 kg. What is the average force ?F that the glove imparts to the ball during the catch?arrow_forwardA 80-kg fisherman in a 133-kg boat throws a package of mass m = 15 kg horizontally toward the right with a speed of v; = 4.0 m/s as in the figure below. Neglecting water resistance, and assuming the boat is at rest before the package is thrown, find the velocity of the boat after the package is thrown. magnitude m/s direction ---Select--- marrow_forwardspace a kg, including suit and oxygen tank. The tether line securing the astronaut to their spacecraft loses its attachment from the spacecraft while they are on a spacewalk. The astronaut is initially at rest with respect to the spacecraft, they then throw their 12.0 kg oxygen tank away from their spacecraft with a speed of 8.00 m/s in order to propel themselves back towards it. I) Calculate the maximum distance they can possibly be from the spacecraft and still return within 2.00 min (the amount of time the air in their helmet remains breathable). II) Which of Newton's law of motion explain best why this strategy works? (a) First (b) Second (c) Thirdarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios