
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The helicopter in the drawing is moving horizontally to the right at a constant velocity. The weight of the helicopter is W=42000 N. The lift force L generated by the rotating blade makes an angle of 21.0° with respect to the vertical. (a) What is the magnitude of the lift force? (b) Determine the magnitude of the air resistance R that opposes the motion.
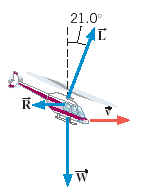
Transcribed Image Text:21.0°
R-
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A stubborn 146 kg mule sits down and refuses to move. To drag the mule to the barn, the exasperated farmer ties a rope around the mule and pulls with his maximum force of 604 N. The coefficients of friction between the mule and the ground are 0.800 for static friction and 0.500 for kinetic friction. Calculate the additional force (in N) that the farmer will need from his son in order to move the mule assuming that the local acceleration due to gravity is 9.80 m/s2.arrow_forwardA flatbed truck is carrying a 30-kg crate up a sloping road at a constant speed. The coefficient of static friction between the crate and the bed is 0.60, and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.25. What is the maximum angle of the slope that the truck can climb if the crate is to stay in place? Answer in degrees.arrow_forwardA block of mass m1 = 3.9 kg is placed on top of a block with mass m2 = 5.4 kg. A force, F = is applied to m2, at an angle 16.1 degrees above the horizontal. If the coefficient of static friction between all moving surfaces is 0.42 and the coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.32, determine the magnitude of the minimum force that will get the blocks moving.arrow_forward
- A heavy sled is being pulled by two people, as shown in the figure. The coefficient of static friction between the sled and the ground is , = 0.579, and the kinetic friction coefficient is = 0.419. The combined mass of the sled and its load is m = 351 kg. The ropes are separated by an angle = 21.0. and they make an angle 0 = 30.1° with the horizontal, Assuming both ropes pull equally hard, what is the minimum rope tension required to get the sled moving? 1214.39 minimum rope tension: incorrect If this rope tension is maintained after the sled starts moving, what is the sled's acceleration? 1.56 acceleration: Attempt 1 N m/s?arrow_forwardA mover is pushing a 148kg box up a ramp. The ramp is inclined at an angle of 30.4 degrees. Since the box is on wheels, assume that friction is negligable. Calculate the force the mover exerts to push the box up the ramp at a constant rate of 1.26 m/s. Assume he pushes parallel to the ramp.arrow_forwardA block with a mass of 7.15 kg is on a horizontal surface that has friction. A string is pulling horizontally on the block with a force of 30.6 N at an angle of 15.2° above horizontal. The block is movingalong the surface at a constant speed of 4.39 m/s. What is the magnitude of the kinetic frictional force that is acting on the block?arrow_forward
- Pahelp po with solution po.arrow_forwardTwo children are pulled on a sled over snow-covered ground. The sled is pulled by a rope that makes an angle of 35° with the horizontal. The children have a combined mass of 45 kg and the sled has a mass of 5.0 kg. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction are u, = 0.20 and µ, = 0.15. Calculate the maximum possible force of static friction between the sled and snow. If the tension in the rope is 95 N, will the sled move? Justify your answer.arrow_forwardYou are pulling your luggage in an air port for an international flight. You know not to pack too much else they charge you extra fees so you weighted your luggage at home to be 21.6 kg. You exert a pull of 49 N in magnitude and at 22 degrees above the horizontal to ensure you can walk at a constant speed on the carpeted floor. What is the coefficient of friction between the caster wheels and the carpet?arrow_forward
- You are pushing a box, apply Fa = 90 N. The box's mass is 25 kg. The coefficients of friction are μs =0.60 and μk = 0.4. The box was stationary when you began pushing. Calculate the frictional force magnitude exerted on the box by the floorarrow_forwardA block with a mass of 4.83 kg is at rest on an inclined surface. The surface makes an angle of 27.9° relative to horizontal. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction are 0.740 and 0.380 respectively. The block remains at rest. What is the magnitude of the frictional force that acts on the block?arrow_forwardA heavy sled is being pulled by two people, as shown in the figure. The coefficient of static friction between the sled and the ground is µs = 0.603, and the kinetic friction coefficient is = 0.403. The combined mass of the sled and its load is m = 336 kg. The ropes are separated by an angle o = 25.0°, and they make an angle 0 = 31.1° with the horizontal. Assuming both ropes pull equally hard, what is the minimum rope tension required to get the sled moving? minimum rope tension: N If this rope tension is maintained after the sled starts moving, what is the sled's acceleration? acceleration: m/s2arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON