
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
The internal loadings at a section of the beam are shown. Determine the in-plane principal stresses at point A. Also, compute the maximum in-plane shear stress at this point.
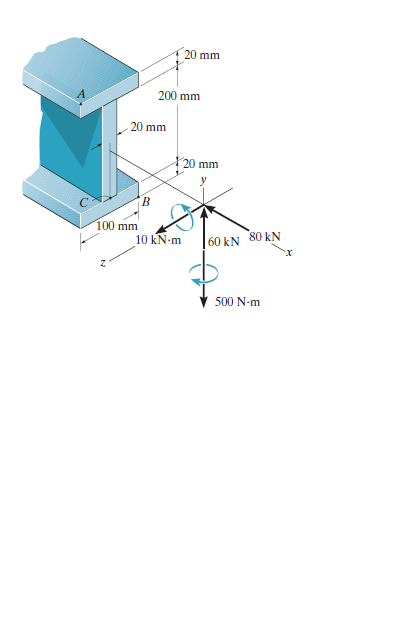
Transcribed Image Text:20 mm
200 mm
20 mm
X20 mm
B.
100 mm
10 kN-m
60 kN 80 kN
500 N-m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3- Calculate the total stresses and show the stress profiles in section A-A due to loading F1 and F2 subjected to the tip section of the arm with length L. A F2 F1arrow_forwardThe wide-flange beam is subjected to the 50-kN force. Determine the principal stresses in the beam at point A located on the web at the bottom of the upper flange. Although it is not very accurate, use the shear formula to calculate the shear stress. A B₂ ➜ 10 mm- B 200 mm 12 mm 250 mm 12 mm -3 m 50 kNarrow_forward2. If the allowable shear stress for each of the steel pins at A and B is tpe 6.5 ksi and the allowable normal stress for bar CB is Operm 10 ksi, determine the diameter of the pins at A and B and that of the square bar CB. Pin A is in double shear while Pin B is in single shear. Ignore points D and E. (^ } 2.5 ft -3 ft -5 ft 150 lb/ft Fx =arrow_forward
- The tube has an inner diameter d; = 20 mm and an outer diameter d, = 22 mm. It is subjected to an internal pressure of 1 MPa and the loads shown below. Determine the stress at point A and draw it on a stress element. 200 mm 400 mm 150 N-m 600 N 1500 N 800 Narrow_forwardThe plate has a thickness of 20 mm and the force P = 3 kN acts along the centerline of this thickness such that d = 150 mm. Plot the distribution of normal stress acting along section a–a.arrow_forwardThe 0.97 in diameter rod is subjected to the loads shown. Determine the normal and shear stress at point B.arrow_forward
- The solid 0.85-in.-diameter rod is subjected to a uniform axial distributed loading along its length of w = 500 lb/ft. Two concentrated loads also act on the rod: P = 1900 lb and Q = 900 lb. Assume a = 12 in. and b = 24 in. Determine the normal stress in the rod at the following locations: (a) x = 8 in. (b) x = 24 in.arrow_forwardThe frame is loaded by a distributed load of intensity q as shown. Consider -25 in. only stress in the bars AC and BC. Each bar has a cross-section that is 0.75 in by 1.5 in. If the allowable normal stress is 5000 psi, determine the maximum allowable value for the distributed load intensity q. 40 in.arrow_forward1. The pictured link acts as a part of the elevator control for a small airplane. If the attached aluminum tube has an inner diameter of 25 mm and a wall thickness of 5 mm, determine the shear stress in the outer and inner surfaces of the tube when a cable force of 600 N is applied to the cables. Also, sketch the shear-stress distribution over the cross-section.arrow_forward
- The U-bar shown below has a circular cross section with a diameter of 1 in. For the loading shown, determine the maximum and minimum normal stresses on a cross section between A and B. 500 lb- A B 2₁ 4 in 500 lbarrow_forwardWhen the stress conditions are given as shown below, calculate the vertical stress and shear stress acting on the ab face.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY