
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781285741550
Author: James Stewart
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
*Identify the location of any discontinuities of f (x) attached
*For each discontinuity, determine the type of discontinuity by evaluating the left- and right-side limits.
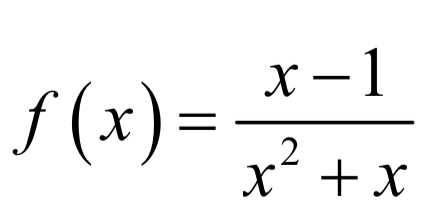
Transcribed Image Text:2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine the intervals on which the function is concave up or down and find the points of inflection. y = 19x + In(x) (x > 0) Provide intervals in the form (*, *). Use the symbol o for infinity, U for combining intervals, and an appropriate type of parenthesis "(", ")", "[", or "]", depending on whether the interval is open or closed. Enter Ø if the interval is empty. Provide points of inflection as a comma-separated list of (x, y) ordered pairs. If the function does not have any inflection points, enter DNE. Use exact values for all responses.arrow_forwardDetermine the intervals on which the function is concave up or down and find the points of inflection. y = 19x2 + In(x) (x > 0) Provide intervals in the form (*, *). Use the symbol ∞ for infinity, U for combining intervals, and an appropriate type of parenthesis "(", ")", "[", or "]", depending on whether the interval is open or closed. Enter Ø if the interval is empty. Provide points of inflection as a comma-separated list of (x, y) ordered pairs. If the function does not have any inflection points, enter DNE. Use exact values for all responses. concave up: concave down: (х, у) %3Darrow_forwardFor each problem, find the x-coordinates of all points of inflection, find all discontinuities, and find theopen intervals where the function is concave up and concave down. y = 1 / ( x-3)arrow_forward
- Graph the function fx) = [4x- 1, if x <-1 Determine if the function is continuous [x-3, if x 2-1 everywhere. Explain how you know.arrow_forwardIdentify three cases for a function NOT to be differentiable at a. Explain why each case fails the conditions of differentiability.arrow_forwardPlease help with question attachedarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134438986
Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134763644
Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781319050740
Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:9781337552516
Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:Cengage Learning