
Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
4th Edition
ISBN: 9781285463247
Author: David Poole
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
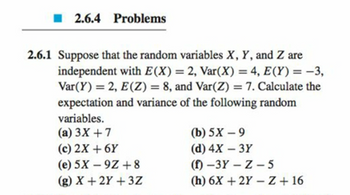
Transcribed Image Text:2.6.4 Problems
2.6.1 Suppose that the random variables X, Y, and Z are
independent with E(X) = 2, Var(X) = 4, E(Y) = -3,
Var(Y)=2, E(Z) = 8, and Var(Z) = 7. Calculate the
expectation and variance of the following random
variables.
(a) 3X+7
(c) 2X+6Y
(e) 5X 9Z+8
-
(g) X+2Y+3Z
(b) 5X-9
(d) 4X - 3Y
(f)-3Y-Z-5
(h) 6X+2Y-Z +16
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Find the equation of the regression line for the following data set. x 1 2 3 y 0 3 4arrow_forwardX and Y are random variables that are the same normally distributed variables as in the previous problem. The Mean of X is 5 and its SD is 3. The Mean of Y is -2 and its SD is 6. You are now being told they are independent. Find the value of each requested parameter. The mean of T= - 3x + 20 is The mean of W= Y - X is The variance of D= X - 2Y isarrow_forwardand Question 2. Suppose Y₁, Y2,, YN is a random sample from a population with mean variance o². Rather than using all N observations, consider an easy estimator of that uses only the first two observations Y* = Y₁ + Y2 2 (1) Show that Y* is a linear estimator. (2) Show that Y* is an unbiased estimator. (3) Find the variance of Y*. (4) Explain why the sample mean of all N observations is a better estimator than Y*.arrow_forward
- 6. Show that 1 s2 E1(Xi – x)² is unbiased estimator of the population variance o? i=1 п-1arrow_forward3. A research assistant is asked to draw two independent normally distributed samples. The first sample, X has a 10 observations with a mean of 1 and sample variance of 2. The second sample, Y has 20 observations with a mean of 0.5 and a sample variance of 3. Test the following hypotheses: (a) X = Ý (b) X > Y (c) Var(X) Var(Y) %3D (d) Var(X) = 1.5 (e) Var(Y) = 2.5 %3Darrow_forward2. [7+3+5+10] Consider the following model where et is i.i.d and |p| < 1. Yt = Bo+B1xt + ut Ut = put-1 + et, t = 1, 2, … … · ‚T, (a) Show that variance of the usual OLS estimator (0² / Σ(x+ - x)²) underestimates the true variance of the OLS estimator. (b) The value of the Durbin-Watson statistic turned out to be 1.4. Compute an estimate of p, the serial correlation parameter, based on the value of the Durbin-Watson statistic. (c) Suppose you also wish to test for serial correlation using Durbin's alternative test (Durbin's h- test) at the 5 percent significance. After estimating the original regression on the entire 80 sam- ples, you saved the residuals and estimated the following auxiliary regression. Et = 0.07 + 0.08æt+ 0.3 êt_1 (0.04) (0.02) (0.1) (Standard errors are in parentheses.) Give the value of the test statistic, and your conclusion (accept or reject the null hypothesis of no serial correlation). (d) Regardless of your answers to parts (a)-(c), suppose you believe that…arrow_forward
- Suppose X and Y are two independent variables with variance 1. Let Z = X+bY where b > 0. If Cor(Z, Y ) = 1/2, what is the value of b?arrow_forward3. An individual who has automobile insurance from a certain company is ran- domly selected. Let Y be the number of moving violations for which the individual was cited during the last 3 years. The pmf of Y is 1 p(y) | .60 .25 .10 .05 What is the variance of Y? Α. 1.1 В. .60 C. .79 D. 1 E. None of the above 4. Based on the pmf in problem 3, what is the probability that an individual was cited between 1 and 3 times (inclusive)? A. .25 В. .05 С. .30 D. .40 E. None of the abovearrow_forward7. Suppose that X is a random variable for which the m.g.f. is as follows: V (1) = (3e' + e) for -0arrow_forward
- Suppose that the probability that a patient admitted in a hospital is diagnosed with a certain type of cancer is 0.03. Suppose that on a given day 10 patients are admitted and X denotes the number of patients diagnosed with this type of cancer. The mean and the variance of X are: None of these E(X)=0.5 and V(X)=0.475 E(X)=0.4 and V(X)=0.384 E(X)=0.3 and V(X)=0.291arrow_forward2. Let x1,x2,...,xn be a random sample from N(0, 2),we wish to estimate the variance σ² as: ²="Is this un unbiased estimator? Find the variance of ²? "arrow_forwardIf X and Y are random variables with variances o = 3 and σ = 9, X and Y are not independent, and oxy = 1, then find the variance of the random variable Z = -9X+8Y - 7.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning
Linear Algebra: A Modern IntroductionAlgebraISBN:9781285463247Author:David PoolePublisher:Cengage Learning Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill
Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...AlgebraISBN:9780079039897Author:CarterPublisher:McGraw Hill Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning
Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...AlgebraISBN:9781337111348Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan NoellPublisher:Cengage Learning

Linear Algebra: A Modern Introduction
Algebra
ISBN:9781285463247
Author:David Poole
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Glencoe Algebra 1, Student Edition, 9780079039897...
Algebra
ISBN:9780079039897
Author:Carter
Publisher:McGraw Hill

Functions and Change: A Modeling Approach to Coll...
Algebra
ISBN:9781337111348
Author:Bruce Crauder, Benny Evans, Alan Noell
Publisher:Cengage Learning