
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
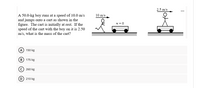
Transcribed Image Text:2.5 m/s
A 50.0-kg boy runs at a speed of 10.0 m/s
and jumps onto a cart as shown in the
figure. The cart is initially at rest. If the
speed of the cart with the boy on it is 2.50
m/s, what is the mass of the cart?
10 m/s
v = 0
A) 150 kg
B 175 kg
c) 260 kg
D 210 kg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Two blocks with masses m1 = 1.4kg and m2 = 4.6kg are at rest on a frictionless surface with a compressed spring between them. When the blocks are let go, block 1 is observed to have a velocity of 4.4m/s to the left. What is the speed of block 2?arrow_forwardA stationary soccer ball of mass m = 0.72 kg is kicked with a constant force of F = 29 N. The woman's foot is in contact with the ball for t = 0.24 s a) Write an expression for the speed of the ball, vi, as it leaves the woman's foot. (b) What is the velocity of the ball right after contact with the foot of the woman?arrow_forwardYou find yourself stuck in outer space with nothing but your physics book and a space suit. You have a mass of 91 kg in your suit, and your physics book has a mass of 2.3 kg. In order to make it back to your stationary spaceship before running out of air, you must move at 0.18 m/s. How fast (in m/s) do you have to throw your physics book to achieve this speed?arrow_forward
- 8) Your mass is 68.8 kg, and the sled s mass is 11.3 kg. You start at rest, and then you jump off the sled, after which the empty sled is traveling at a speed of 3.10 m/s. What will be your speed on the ice after jumping off? Question 8 options: 0.36 m/s 0.71 m/s 0.61 m/s 0.51 m/s 9) Your mass is 87.6 kg, and the sled s mass is 14.4 kg. The sled is moving by itself on the ice at 3.16 m/s. You parachute vertically down onto the sled, and land gently. What is the sled s velocity with you now on it? Question 9 options: 0.45 m/s 0.32 m/s 0.77 m/s 0.61 m/sarrow_forwardA 3.45 kg black ball traveling 4 m/s has a head on collision with a white one at rest. Using the velocities shown, calculate the mass of the white ball, Ignore friction and air resistance. 0 m/s 4 m/s 1.4 m/s 5.7 m/sarrow_forwardMomentum = mass (Kg) times velocity (m/s). Why does a train longer to stop than a car?arrow_forward
- A 9 kg steel ball strikes a wall with a speed of 4.98 m/s at an angle of 30.7° with the normal to the wall. It bounces off with the same speed and angle, as shown in the figure. y 4.98 m/s 30.7° * 30.7° 9 kg 9 kg 1.98 m/s x If the ball is in contact with the wall for 0.255 s, what is the magnitude of the average force exerted on the ball by the wall? Answer in units of N. Your response... i Previous Responses X #1. 201.5089 PALETTEarrow_forwardTwo spring-loaded carts are at rest on a low-friction track. The spring is released, pushing the carts away from each other. Positive to the right and negative to the left. The bricks on top of the carts have the same mass as the cart. The blue cart has a speed of 1m/s after the spring is released. Calculate the velocity of the red car after the explosion Before Explosion After Explosion + 5 m/s - 5 m/s +3 m/s O - 3 m/s O +1.5 m/sec O - 1.5 m/secarrow_forwardYour mass is 63.2 kg, and the sled s mass is 21.7 kg. You start at rest, and then you jump off the sled, after which the empty sled is traveling at a speed of 4.27 m/s. What will be your speed on the ice after jumping off? 1.47 m/s 0.88 m/s 2.06 m/s 1.77 m/sarrow_forward
- 27arrow_forwardQuestion 15 The graph shows momentum, p, versus time, t, for a spacecraft while it is firing its rocket engines in space. What does the slope of this graph represent? K O the work done on the spacecraft the mass of the spacecraft the net force on the spacecraft the velocity of the spacecraft None of the abovearrow_forwardthis is a practice problem, not a graded assignmentarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON