
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
2.3 Kg/s of solid containing 0.55 Kg/s soluble material is to be washed with 2.8 Kg/s pure solvent in a counter – current unit . The final residue is to contain not more than 0.1% solute when dried . Find the number of stages given that the amount of solution in under flow varies with solute concentration according to the relation : W = 0.2 X + 0.3 , Also find the concentration and quantities in and out from each stage .
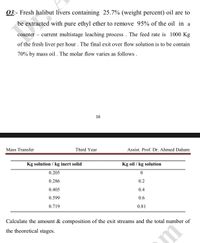
Transcribed Image Text:03:- Fresh halibut livers containing 25.7% (weight percent) oil are to
be extracted with pure ethyl ether to remove 95% of the oil in a
counter
current multistage leaching process . The feed rate is 1000 Kg
of the fresh liver per hour . The final exit over flow solution is to be contain
70% by mass oil . The molar flow varies as follows .
16
Mass Transfer
Third Year
Assist. Prof. Dr. Ahmed Daham
Kg solution / kg inert solid
Kg oil / kg solution
0.205
0.286
0.2
0.405
0.4
0.599
0.6
0.719
0.81
Calculate the amount & composition of the exit streams and the total number of
the theoretical stages.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A sheet of steel with 100cm2 area has nitrogen(N2) atmospheres on both sides and is permitted to achieve a steady-state diffusion condition. In order to increase the flow rate of N2, which of the following modifications is useful? Steel sheet O Increase the N2 pressure at C1 O Decrease the temperature. O Increase the N2 pressure at C2 O Increase the thickness of the steel sheet.arrow_forward2.3 Kg/s of solid containing 0.55 Kg/s soluble material is to be washed with 2.8 Kg/s pure solvent in a counter – current unit . The final residue is to contain not more than 0.1% solute when dried . Find the number of stages given that the amount of solution in under flow varies with solute concentration according to the relation : W = 0.2 X + 0.3 , Also find the concentration and quantities in and out from each stage . subject is mass transfer, leaching processarrow_forward3)Gas absorption (scrubbing) is an operation in which gas mixture is contacted with a liquid for the purpose of preferentially dissolving one or more components of the gas mixture and to provide a solution of them in the liquid phase. (b)What are the differences between Physical Absorption and Chemical Absorption?Demonstrate their effects on gas absorptionprocessarrow_forward
- Consider a solid sphere, of radius R, which is placed in a large body of unstirred, aqueous solution, as shown in Figure 1. The dissolution of the solid A, is slow enough that quasi-steady-state can be assumed. Given the solubility of A in the solution is CA* at the surface of the sphere and assume there is a bulk diffusion in the solution (i.e. the term yA(NA+Nu) is not zero). 1.) Derive an expression for the concentration distribution of A in the solution; and 2.) develop a mathematical relationship for molar flow rate of A, entering the solution at the surface of the sphere. FLUID SOLID 'A' &r Rsarrow_forwardA double effect evaporator is used to concentrate an 18% CuSO4 solution. At the end of evaporation, 26,000 kg/h of 50% CuSO4 solution were obtained. If the water evaporated in the second effect is half the water evaporated in the first effect, determine: a) The amount of solution fed into the first effect. b) The amount of water evaporated in the first and second effect. c) The amount of solution fed into the second effect, as well as its composition. Problem diagram 18% CuSO4 82% H₂O M₁ M₂ M3 X CuSO4 Y H₂O A 2 M4 = 0.5 M₂ M5 H₂O steam M6 M2 M6 is the water that condenses 26 000 kg/hr 50% CuSO4 50% H2₂Oarrow_forwardConsider a diffusion process in a semi-infinite solid with a source at x=0 mm, the concentration of the diffusing species is 2 nm-3 at x=5 mm and t=1 hr (since the start of the process). At what time the concentration at x=15 mm will reach 3 nm-3 ?arrow_forward
- A new type of porous material serves as food packaging film, as shown in the figure below. The film rests on a nonporous metal plate. The packaging film is 0.20 cm thick (2.0 mm). The food contains liquid water, which exerts a vapor pressure of 0.030 atm at 25°C. At 25°C, the effective diffusion coefficient of water vapor in the porous film is 1.3 x 10^-4 cm/s, and the molecular diffusion coefficient of water vapor in air is 0.26 cm/s. You may assume that the total system pressure is constant at 1.0 atm, and initially, the gas space of the porous film contains air and no water vapor. How long will it take for the water vapor to achieve a partial pressure of 0.0150 atm at the back surface of the film (z = 0) at 25°C?arrow_forwardThe aqueous acetone solution is mixed with Methyl isobutyl (MIB) solvent containing 3% acetone by mass. The flow rates of the upper and lower currents leaving the system are 1000 kg/h and 400 kg/h, respectively. System the proportion of acetone in the upper and lower leaving current is 15% and 10% by weight, respectively. The phase separation of the refinate and the extract takes place. According to this a. Calculate the composition and amount of the aqueous acetone solution entering the system. b. Calculate the amount of Methyl isobutyl ketone (MIBK) solvent containing 3% acetone sent to the system. extract phase Data; Methyl isobutyl (MIB 0.05 0.05 0.06 0.07 0.08 0.09 0.20 XA Acetone 0 0.05 0.15 0.20 0.25 0.35 0.43 XC. Methyl isobutyl (MIB 0.95 0.94 0.89 0.84 0.79 Refining phase 0.69 0.59 YA Acetone 0 0.02 0.10 0.15 0.20 0.30 0.40 YCarrow_forwardConsider a metal spherical vessel, with an inner diameter of 5 m and a thickness of 3 mm, containing hydrogen gas at 2000 kPa. The vessel is situated in a room with atmospheric air at 1 atm. The ventilation system for the room can keep the air fresh, provided that the rate of hydrogen leakage is below 5 μg/s. If the diffusion coefficient and solubility of hydrogen gas in the metal vessel are 1.5 × 10−12 m2/s and 0.005 kmol/m3·bar, respectively, determine whether the vessel is safely containing the hydrogen gasarrow_forward
- A wet sphere of gelatin gel at a temperature of 20 "C contains a uniform concentration of urea of 0.05 kg mol/m'. The sphere has a diameter of 16 mm. The sphere is suddenly immersed in turbulent water which initially contains urea of concentration 0.1 kg mol/m'. The diffusion coefficient of the urea in the gelatin gel is 8.59 * 10*" m/s. The convective mass transfer coefficient ke is 1.07375 x 10 m/s and the equilibrium distribution coefficient K is 1. For radial mass transfer only, listing your assumptions, calculate, (a) the concentration at a distance of 4,8 mm from the midpoint of the sphere after 25.87 hours of mass transfer. (b) the time by which the concentration, c, at the centre of the sphere is 0.09975 kg mol/m3arrow_forwardFind the diffusion coefficient of ammonia-hydrogen system at 25 °C and atmospheric pressure and correct its value for 85 °C and compare it with experimental values.arrow_forwardA quiescent body of water has a depth of 600 mm. The DO level at the bottom after 16 days is 3.5 mg/l when the surface is exposed to the atmosphere at a temperature of 25o Determine the DO of the water body. The saturated DO at 25oC is 8.5 mg/l and the diffusion coefficient (kd) at 25oC is 2.5 x 10-3 mm2/s.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The