
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
(a) Can the circuit shown in Figure be reduced to a single resistor connected to the batteries? Explain. (b) Calculate each of the unknown currents I1, I2, and I3 for the circuit.
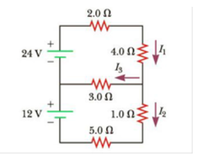
Transcribed Image Text:2.0 Ω
24 V
4.0 Ω.
Is
3.0 Ω
12 V
1.0 Ω.
5.0 Ω
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The figure below shows five resistors and two batteries connected in a circuit. What are the currents I,, I,, and I,? (Consider the following values: R, = 1.04 0, R, = 2.10 0, R3 = 3.20 0, R, = 4.20 N, R, = 6.20 N. Due to the nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values in your calculations-including answers submitted in WebAssign. Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) A I2 A I3 = A R5 12.0 V R2 9.00 V R43 Rarrow_forwardWhen different resistors are connected in parallel across an ideal battery, we can be certain that a the same current flows in each one. b the potential difference across each is the same. c the power dissipated in each is the same. d their equivalent resistance is greater than the resistance of any one of the individual resistances. e their equivalent resistance is equal to the average of the individual resistances.arrow_forwardRegarding the circuit in the left-hand part of the diagram: a) What is the current passing through each of the resistors? b) What is the current supplied by the battery? c) What is the potential difference across the 12 Ω resistor? d) How much power is turned to heat in the 4 Ω resistor? e) If we replace the circuit on the left by the one in the right-hand part of the diagram, with the same battery and only one resistor, what resistance Req should we choose to obtain the same total current?arrow_forward
- A circuit consisting of three ideal batteries with voltages 81, 82, and 83, and three ideal resistors with resistances R1, R2, and R3, is shown in the figure. Calculate the current Ip through point P. Let the sign of the current correspond to its direction, with "up" being positive. 81= 14.5 V, &2 = 19.5 V, 83 = 28.5 V Ry R2 R =4.30 kQ, R = 21.0 kQ, R = 3.00 k2 mA Ip =arrow_forwardUse the exact values you enter to make later calculations. The figure below shows a battery connected to a circuit. The potential difference across the battery and the resistance of each resistor is given in the figure. (Assume R1 = 11.5 Ω, R2 = 1.30 Ω, and V = 6.50 V.) (I skipped parts a-f) (g) Using the result from part (f) and the battery's potential difference, what is the magnitude of the potential difference (in V) across the 3.00 Ω resistor? in V (h) What is the current (in A) in the 3.00 Ω resistor? in Aarrow_forwardThree resistors, R₁ = 232, R₂=3502, and R,=4552, are connected to a capacitor of capacitance C=32μF and a battery with emf 8=14V as shown in the figure below. The capacitor is initially uncharged when the switch is closed at t-0. Determine the current running on R, on the capacitor at r=0. Express your answer in units mA using zero decimal places. S w ++ R₁ www C ww R3arrow_forward
- A circuit is constructed with six resistors and two batteries as shown. The battery voltages are V₁ = 18 V and V₂ = 12 V. The positive terminals are indicated with a + sign, The values for the resistors are: R₁ = R5 = 64 02, R₂ = R₁ = 157 02 R₂ = 54 02, and R4 = 65 02. The positive directions for the currents 1₁, 12 and 13 are indicated by the directions of the arrows. H I₁ I₂ I3 a •V₁ R₂ Ro b "V₂ 2 R4 5arrow_forwardUse the exact values you enter to make later calculations. The figure below shows a battery connected to a circuit. The potential difference across the battery and the resistance of each resistor is given in the figure. (Assume R1 = 11.5 Ω, R2 = 1.30 Ω, and V = 6.50 V.) (I skipped a-c) (d) Using the result from part (c), what is the equivalent resistance (in Ω) of the entire circuit? in Ω (e) What is the current (in A) through the battery (equivalently, the conventional current that exits the positive terminal of the battery and enters the R2)? in A (f) What is the magnitude of the potential difference (in V) across R2? in Varrow_forwardThe figure below shows five resistors and two batteries connected in a circuit. What are the currents I,, I2, and I3? (Consider the following values: R, = 1.08 0, R2 = 2.20 0, R3 = 3.18 0, R4 = 4.04 0, R5 = 6.06 0. Due to the nature of this problem, do not use rounded intermediate values in your calculations-including answers submitted in WebAssign. Indicate the direction with the sign of your answer.) A A I3 = A Rs R3 12.0 V R2 9.00 V R1arrow_forward
- show full and complete procedure please HANDWRITTEN onlyarrow_forwardinternal resistors r1 and r2 are both 0.2n. εί Consider the circuit diagram depicted in the figure. It is known that two 25Ω 24V and ε2 36V. R2 and R3-40f, but Ri is unknown. Caution: Current directions. You will lose all the points, if you use a wrong number to start with, so it is important that you get all the result subproblems. s right before you move on to next What equation do you get when you apply the loop rule to the loop abcdefgha If the current through the top branch is 12 0.1 A, what is the current through in terms of the variables in the figure? the bottom, 13, in amps? the voltage across R1, and point out which point, a or e has a higher potential. Find Find the resistance of R1. Find the voltage Va Ve between points a and & 12 R2 R3 13 e2arrow_forwardIn the circuit below, all four resistors are identical (R, = R2 = R3 = R4 = R) and the battery has a voltage of 5.06 V. R1 R2 V R3 R4 (a) When the switch is placed in position 1, the measured current in the battery is 1.2 mA. What is the value of each resistor? kΩ (b) When the switch is placed in position 2, what is the current flowing out of the battery? (c) When the switch is open (neither in position 1 or position 2), what is the current flowing out of the battery?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON