
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
The second-order liquid phase reaction
C6 H 5COCH2Br + C6H5N⎯⎯→C6H5COCH2NC5H5Br
is carried out in a batch reactor at 35°C. The specific reaction-rate constant is 0.0445 dm3/mol/min.Reactor 1 is charged with 1,000 dm3, where the concentration of each reactant after mixing is 2M.
What will be the conversion and concentration of each species in reactor 1 after 10, 50, and 80minutes in the reactor that is being drained?
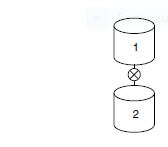
Transcribed Image Text:2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Consider the table of data collected for the reaction A → Products. Calculate the rate constant for this reaction. Show work. Time (s) [A] M In [A] 1/[A] 0.6 -0.51083 1.666667 0.5 0.325 -1.12393 3.076923 1 0.178 -1.72597 5.617978 1.5 0.095 -2.35388 10.52632 2 0.05 -2.99573 20 2.5 0.028 -3.57555 35.71429 3 0.015 -4.19971 66.66667 3.5 0.008 -4.82831 125 4 0.004 -5.52146 250arrow_forwardLooking at this reaction @ STP: 4 K (s) + O2 (g) à 2 K2O (s) if you burn 3.00 moles of K, how many moles of O2 are used up? 1.50 moles 0.50 moles 0.75 moles 1.00 moles None of the abovearrow_forwardPlease help!!! (Gpt/Ai wrong ans not allowed)arrow_forward
- the gas phase reaction A+B<-->C+D takes place in a batch reactot at 300C. The eq constant k at 300C is 9.0.The reactor is initially charged with 6mol A and 6mol B. What is the extent of the reaction at eq ? What are the mole fractions of each gas ?arrow_forwardSolve correctly please. I know the final answer,but need steps to find it with explanation.arrow_forwardquestion 3 in imageeearrow_forward
- H1arrow_forwardA reaction with an activation energy of 94.8 kJ/mol is carried out at 281. K and 376. K. The reaction rate at 376. K is a) should be the same as at the other temperature b) approximately 1.338 times faster than at 281. K c) approximately 2.821e+4 times faster than at 281. K d) approximately 6.496e+4 times faster than at 281. Karrow_forwardA8arrow_forward
- 17. The reaction A+B→C+D is carried out at 80 °C in an isothermal, perfectly stirred tank batch reactor. The reaction rate can be described as second-order, where k=0.058 m³ kmol-¹ min¹¹. At 80 °C, 240 kg of material A (MÃ=60 g mol-¹) and 400 kg of material B (M³=80 g mol-¹) is added into the stirred tank. At this point, the volume of the (liquid) reaction mixture is 0.9 m³. The reaction does not change the volume. How much time is required to reach 95% conversion? batch reactorarrow_forwarda) The new engineer you hired suggests operating the reactor at atmospheric pressure (instead of 300kPa) while keeping the temperature constant (at 800 K) to increase the conversion to product “C”.Would decreasing the pressure increase the conversion? Why?b) Would you consider using an inert gas (such as argon) while keeping the T and the P constant toincrease the conversion? Why?c) Is this reaction endothermic or exothermic? List two benefits of operating the reactor at 800 K?Explain with reactions pleasearrow_forwardYou are carrying out a reaction in the laboratory. You need to convert 1.00 mole of reactant X into products. This reaction shows first-order kinetics, and the reaction mixture has a constant volume of 1.00 L. At 1:00pm, you start the reaction at 25\deg C with 1.00 mole of reactant X. At 2:00pm, you find that 0.70 moles of reactant X remain. You immediately increase the temperature of the reaction mixture to 35\deg C. At 3:00pm, you discover that 0.25 moles of reactant X are still present. You want to be able to finish the reaction by 4:00pm, but you cannot stop the reaction until only 0.01 moles of reactant X remain. You must increase the temperature again. What is the minimum temperature required to complete the reaction by 4:00pm? (Remember, the reaction is complete when only 0.01 moles of X remain.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The