
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
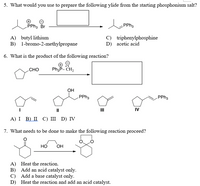
Transcribed Image Text:5. What would you use to prepare the following ylide from the starting phosphonium salt?
PPH3 Br
PPhs
A) butyl lithium
B) 1-bromo-2-methylpropane
C) triphenylphosphine
D) acetic acid
6. What is the product of the following reaction?
CHO
PhP- CH,
OH
PPH3
PPH3
II
II
IV
А) I B) П С) II D) IV
7. What needs to be done to make the following reaction proceed?
но
OH
A) Heat the reaction.
B) Add an acid catalyst only.
C) Add a base catalyst only.
D) Heat the reaction and add an acid catalyst.
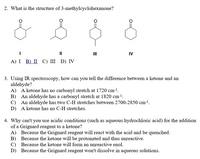
Transcribed Image Text:2. What is the structure of 3-methylcyclohexanone?
II
II
IV
А) I B) П С) II D) IV
3. Using IR spectroscopy, how can you tell the difference between a ketone and an
aldehyde?
A) A ketone has no carbonyl stretch at 1720 cm-!.
B) An aldehyde has a carbonyl stretch at 1820 cm-1.
C) An aldehyde has two C-H stretches between 2700-2850 cm-1.
D) A ketone has no C-H stretches.
4. Why can't you use acidic conditions (such as aqueous hydrochloric acid) for the addition
of a Grignard reagent to a ketone?
A) Because the Grignard reagent will react with the acid and be quenched.
B) Because the ketone will be protonated and thus unreactive.
C) Because the ketone will form an unreactive enol.
D) Because the Grignard reagent won't dissolve in aqueous solutions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Identify the compound with an acetal functional group. II OH A) I Но B) II II OH IV C) II OH O. D) IV 2:16 PM 67% 31°F 底 3/29/2022 P Type here to search PrtSc Insert Dele F8 F9 F10 F11 F12 F6arrow_forward2. Show how 1-butanol can be converted into the following compounds: (a) (b) CNarrow_forward2) Use compound C (shown below) to answer the following questions. H2N H CH3 compound C H" H3C Br a) Classify compound C as a primary, secondary or tertiary amine. b) Give the IUPAC name for compound C, omitting absolute configuration (R or S) designations. c) In the indicated spaces below, draw the enantiomer, a diastereomer and a Fischer projection of compound C. enantiomer of compound C diastereomer of compound C Fischer projection of compound Carrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY