
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
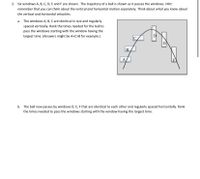
Transcribed Image Text:2. Six windows A, B, C, D, E and F are shown. The trajectory of a ball is shown as it passes the windows. Hint:
remember that you can think about the vertical and horizontal motion separately. Think about what you know about
the vertical and horizontal velocities.
a. The windows A, B, C are identical in size and regularly
spaced vertically. Rank the times needed for the ball to
pass the windows starting with the window having the
largest time. (Answers might be A=C>B for example.)
D
E
B.
A
b. The ball now passes by windows D, E, F that are identical to each other and regularly spaced horizontally. Rank
the times needed to pass the windows starting with the window having the largest time.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- E7. A ball is thrown upward with an initial velocity of 14 m/s. Using the approximate value of g = 10 m/s^2, what are the magnitude and direction of the ball’s velocity a. 1 second after it is thrown? b. 2 seconds after it is thrown? E8. How high above the ground is the ball in exercise 7 a. 1 second after it is thrown? b. 2 seconds after it is thrown? only need question 8, the rest is for referencearrow_forward1. A person kicks a ball horizontally off of a cliff 8.3 m high and it lands 22 m away on the beach. a) Sketch the situation here with labeled events b) How long does the ball take to land? c) What was the initial velocity of the ball? d) How would the time change for the ball to hit the beach if the person hit it really hard? How about if they just let it drop? Explain your answer with sketches and words. hit horizontally dropped hit harder horizontallyarrow_forward1. Draw a qualitative motion diagram (including both velocity and acceleration vectors) for the following objects in the following situations: Be sure to show the vector subtraction that supports how you got your acceleration vectors. a) Viewed from above, a car traveling around a traffic circle having radius R at constant speed. b) A person in a perfectly circular roller coaster loop-de loop having radius R. (Note: higher speed at the bottom of the loop than the top)arrow_forward
- 4. A ball is shot from a cannon at 50 m/s at an angle of 30° above the horizontal. a. Draw a labeled diagram with all relevant information. Note directions you chose to be +x and +y. b. How far has the ball traveled horizontally when it reaches its highest point in the flight? How high is it at this point? c. What is the speed of the ball at the highest point in its flight?arrow_forwardQ2. A plane has an airspeed of 915 km/h. The pilot sets the heading at [S34°E]. There is an 84 km/h wind headed [W12°N]. [A7, C4] a) Draw and label the vector diagram for the wind and plane's velocities. b) Calculate the velocity of the plane as seen by an observer on the ground.arrow_forwardA 54 g ice cube can slide without friction up and down a 30∘ slope. The ice cube is pressed against a spring at the bottom of the slope, compressing the spring 10 cm. The spring constant is 23 N/m . When the ice cube is released, what total distance will it travel up the slope before reversing direction? Δs = 43 cm The ice cube is replaced by a 54 g plastic cube whose coefficient of kinetic friction is 0.20. How far will the plastic cube travel up the slope? ?????arrow_forward
- Whale sharks swim forward while ascending or descending. They swim along a straight-line path at a shallow angle as they move from the surface to deep water or from the depths to the surface. In one recorded dive, a shark started 50 m below the surface and swam at 0.85 m/s along a path tipped at a 13° angle above the horizontal until reaching the surface. a. What was the horizontal distance between the shark's starting and ending positions?arrow_forwardinclude a picture or description of your coordinate system (origin, positive direction).arrow_forwardA ball is thrown at an initial height of 90 feet at an initial velocity of 55 feet/second at an angle of 75 degrees. Given the parametric equations y = 16t2 + Vo · Sin(0)t + ho and r = Vo Cos(0)t. When doing calculations, carry 5 digits of accuracy, so your round off does not build up. a. What is the ball's height in 3 seconds? feet. b. When will the object hit the ground? seconds. c. How far horizontally will the ball be when it hits the ground? feet. d. When will the ball be at its maximum height? seconds. e. What is the ball's maximum height? feet. f. How far horizontally will the ball be when it reaches its maximum height? feetarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON