
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
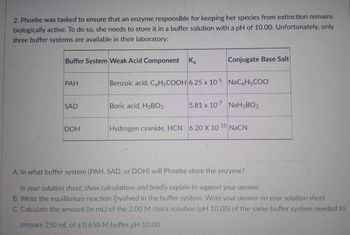
Transcribed Image Text:2. Phoebe was tasked to ensure that an enzyme responsible for keeping her species from extinction remains
biologically active. To do so, she needs to store it in a buffer solution with a pH of 10.00. Unfortunately, only
three buffer systems are available in their laboratory:
Buffer System Weak Acid Component
Ka
Conjugate Base Salt
PAH
Benzoic acid, C6H5COOH 6.25 x 10-5 NaC6H5COO
SAD
Boric acid, H3BO3
5.81 x 107 NaH₂BO3
DOH
Hydrogen cyanide, HCN 6.20 X 10-10 NaCN
A. In what buffer system (PAH, SAD, or DOH) will Phoebe store the enzyme?
In your solution sheet, show calculations and briefly explain to support your answer.
B. Write the equilibrium reaction involved in the buffer system. Write your answer on your solution sheet
C. Calculate the amount (in mL) of the 2.00 M stock solution (pH 10.00) of the same buffer system needed to
prepare 250 mL of a 0.650 M buffer pH 10.00.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following aqueous solutions are good buffer systems? 0.10 M nitrous acid + 0.13 M sodium nitrite 0.31 M ammonium bromide + 0.31 M ammonia 0.29 M hydroiodic acid + 0.23 M potassium iodide 0.16 M potassium fluoride + 0.21 M hydrofluoric acid O 0.39 M acetic acid + 0.25 M potassium acetatearrow_forwardGW 18b 1. A 20.0 mL sample of a 0.240 M hydrofluoric acid (HF) solution is titrated with 0.200 M NaOH. Determine: (a) pH of the acid solution before any base is added; (b) volume (in mL) of base needed to get to the equivalence point; (c) pH halfway to equivalence point; (d) pH at equivalence point; (e) pH when 0.100 mL NaOH is added beyond the equivalence point. (K₂ of HF = 7.1 × 104)arrow_forwardOne of the buffer systems the human body has to regulate pH is based on the phosphate anion. If blood has a pH of 7.40, and the three Ka values for phosphoric acid are 7.52 × 10−3, 6.23 × 10−8, and 4.8 × 10−13, write the chemical equilibrium equation showing the phosphate species that are involved in this buffer.arrow_forward
- Please solve the question step by step and way with the correct answer.arrow_forward5mL of 0.150 M ammonia (NH3) is titrated with 0.100 M hydrochloric acid (HCl) The Kb for ammonia is 1.75 x 10-5 1)Write a balanced chemical equation for the reaction of ammonia and hydrochloric acid and a balanced chemical equation for the equilibrium of ammonia in water. 2) What is the pH of the ammonia solution prior to the addition of any HCl?arrow_forwardWhich of the following aqueous solutions are good buffer systems? O 0.36 M hydrofluoric acid + 0.23 M potassium fluoride O 0.27 M hydrochloric acid + 0.22 M sodium chloride O 0.15 M potassium hydroxide + 0.24 M potassium chloride O 0.15 M hydrocyanic acid + 0.15 M sodium cyanide O 0.27 M ammonium bromide + 0.33 M ammoniaarrow_forward
- Chemistry (Part -3) =============arrow_forwardDetermine the concentration of CH NH¸* in a buffer solution by constructing an ICE table, writing the equilibrium constant expression, and use this information to determine the concentration of CH NH+. The Kb for CH NH₂ is 3.8 × 10-10. Complete Parts 1-3 before submitting your answer. 2 1 2 3 NEXT > 2 A buffer solution contains dissolved CH NH and CH NH Cl. The initial concentration of CH NH2 is 0.50 M. The pH at equilibrium of the buffer is 4.20. Let x represent the original concentration of CH NH+ in the water. Fill in the ICE table with the appropriate value for each involved species to determine concentrations of all reactants and products. Initial (M) Change (M) Equilibrium (M) CH NH2(aq) + H₂O(I) = OH(aq) + C HẠNH, (aq) RESET 0 0.50 x 4.20 -4.20 6.3 x 10-5 -6.3 x 10-5 1.6 × 10-10 -1.6 × 10-10 3.8 × 10-10 -3.8 × 10-10 x +4.20 x-4.20 x + 6.3 x 10-5 x - 6.3 × 10-5 x + 1.6 × 10-10 x-1.6 × 10-10 x + 3.8 × 10-10 x - 3.8 × 10-10arrow_forwardA 29.6 mL sample of 0.271 M dimethylamine, (CH3)2NH, is titrated with 0.237 M hydrobromic acid. After adding 12.9 mL of hydrobromic acid, the pH is Use the Tables link in the References for any equilibrium constants that are required.arrow_forward
- + pH Changes in Buffers When a solution contains a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid, it will be a buffer solution. Buffers resist change in pH following the addition of acid or base. A buffer solution prepared from a weak acid (HA) and its conjugate base (A) is represented as HA (aq) → H¹ (aq) + A (aq) The buffer will follow Le Châtelier's principle. If acid is added, the reaction shifts to consume the added H+, forming more HA. When base is added, the base will react with H+, reducing its concentration. The reaction then shifts to replace H+ through the dissociation of HA into H+ and A™. In both instances. [H] tends to remain constant. The pH of a buffer is calculated by using the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation: A] pH =pK₂ +log HA ▼ Part A pH = What is the pH of a buffer prepared by adding 0.607 mol of the weak acid HA to 0.507 mol of NaA in 2.00 L of solution? The dissociation constant K₁ of HA is 5.66 x 10-7 Express the pH numerically to three…arrow_forwardCalculate the change in pH when 0.280 mol H+ is added to 1.00 L of each of the following buffers If the final pH is lower than the initial, your answer should be a negative number. a 0.540 M solution of pyridine (py) containing 0.500 M pyH+change in pH = If the final pH is lower than the initial, your answer should be a negative number. a 0.620 M solution of aniline (an) containing 0.920 M anH+change in pH =arrow_forwardFor different enzymes, there is an optimum pH at which the enzyme is most active. For example, for enzymes of gastric juice optimum pH 1-2, for duodenal enzymes pH 7.7, for liver enzymes pH 9.5, etc. Determine which medium (a or b) is most favorable for each of the enzymes mentioned above if the following substances are added to 1.0 liter of water: a) 0.040 mol KOH and 0.030 mol HBr; b) 4.0 10-9 mol HNO3. Neglect the change in the volume of the solution. Confirm your answer with calculations.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY