
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science (9th Edition)
9th Edition
ISBN: 9780134746241
Author: Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
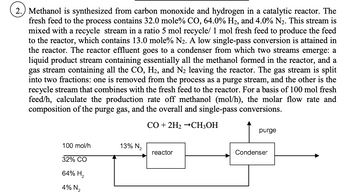
Transcribed Image Text:2.) Methanol is synthesized from carbon monoxide and hydrogen in a catalytic reactor. The
fresh feed to the process contains 32.0 mole% CO, 64.0% H₂, and 4.0% N₂. This stream is
mixed with a recycle stream in a ratio 5 mol recycle/ 1 mol fresh feed to produce the feed
to the reactor, which contains 13.0 mole% N₂. A low single-pass conversion is attained in
the reactor. The reactor effluent goes to a condenser from which two streams emerge: a
liquid product stream containing essentially all the methanol formed in the reactor, and a
gas stream containing all the CO, H₂, and N₂ leaving the reactor. The gas stream is split
into two fractions: one is removed from the process as a purge stream, and the other is the
recycle stream that combines with the fresh feed to the reactor. For a basis of 100 mol fresh
feed/h, calculate the production rate off methanol (mol/h), the molar flow rate and
composition of the purge gas, and the overall and single-pass conversions.
CO + 2H₂ →CH3OH
100 mol/h
32% CO
64% H₂
4% N₂
13% N₂
reactor
purge
Condenser
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Recommended textbooks for you
 Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...Earth ScienceISBN:9780134746241Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON
Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134041360Author:Greg CarbonePublisher:PEARSON Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Environmental ScienceEarth ScienceISBN:9781260153125Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON
Earth Science (15th Edition)Earth ScienceISBN:9780134543536Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. TasaPublisher:PEARSON Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)Earth ScienceISBN:9781337569613Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott SpoolmanPublisher:Cengage Learning Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Physical GeologyEarth ScienceISBN:9781259916823Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, LisaPublisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Applications and Investigations in Earth Science ...
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134746241
Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:PEARSON

Exercises for Weather & Climate (9th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134041360
Author:Greg Carbone
Publisher:PEARSON

Environmental Science
Earth Science
ISBN:9781260153125
Author:William P Cunningham Prof., Mary Ann Cunningham Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Earth Science (15th Edition)
Earth Science
ISBN:9780134543536
Author:Edward J. Tarbuck, Frederick K. Lutgens, Dennis G. Tasa
Publisher:PEARSON

Environmental Science (MindTap Course List)
Earth Science
ISBN:9781337569613
Author:G. Tyler Miller, Scott Spoolman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physical Geology
Earth Science
ISBN:9781259916823
Author:Plummer, Charles C., CARLSON, Diane H., Hammersley, Lisa
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,