
College Algebra
1st Edition
ISBN: 9781938168383
Author: Jay Abramson
Publisher: OpenStax
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I need help with this problem and an explanation of the solution for the image described below. (Statistics: Engineering Probabilities)
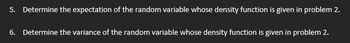
Transcribed Image Text:5. Determine the expectation of the random variable whose density function is given in problem 2.
6. Determine the variance of the random variable whose density function is given in problem 2.
![2. Let X be a continuous random variable with probability density function
f(x)
=
1
π[1 + (x − 1)²]
-
for-co< x < ∞o. Find the cumulative distribution function.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/ea56b2d3-976b-48ba-b1de-ef5a4d536379/279f8ee9-d938-41a8-a1e1-af84d601d0f6/fqldnzx_thumbnail.jpeg)
Transcribed Image Text:2. Let X be a continuous random variable with probability density function
f(x)
=
1
π[1 + (x − 1)²]
-
for-co< x < ∞o. Find the cumulative distribution function.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Recall that the general form of a logistic equation for a population is given by P(t)=c1+aebt , such that the initial population at time t=0 is P(0)=P0. Show algebraically that cP(t)P(t)=cP0P0ebt .arrow_forward. Find the expected value of the Probability density function: ƒ(x)= 24 (3x)(4 — x) - 64 on the interval of [0,4]. Then find V(x), and oarrow_forwardLet X and Y be independent random variables with joint probability density function fxy(x, y) = 1/3 (x + y), 0 < x <= 2, and 0 < y<= 1, and 0 otherwise. The marginal pdf fx(x) is given by O a. O b. O c. O d. (2 +2X)/3 (2 + 2X)/3 (X+1/2)/3 (X+1/2)/3 0 < X<= 2 0< X<= 1 0 < X<= 1 0arrow_forward
- The velocity of a particle in a gas is a random variable X with probability distribution fx(x) = 32x²e-4x The kinetic energy of the particle is Y = 1/mX². Suppose that the mass of the particle is 64 yg. Find the probability distribution of Y. (Do not convert any units.) x >0.arrow_forwardSuppose that the random variables X and Y have the following joint probability density function. f(x, y) = ce-6x-2y, 0 < y < x. (a) Find P(X < 2, Y < (b) Find the marginal probability distribution of X.arrow_forwardSuppose that X and Y have the following joint probability density function. f(x, y) = ₁34y, 0 0, x − 2 < y < x + 2 154, (a) Find E(XY). (b) Find the covariance between X and Y. Round your answer to 4 decimals. Round your answer to 4 decimals.arrow_forward
- C1. Let X be a continuous random variable with PDF f(x) = ? (2 – a) for –1 1)? (c) Calculate the expectation and variance of X. (d) Let Y (X2 – 1). What is the expectation of Y?arrow_forwardA continuous random variable, X, has the following probability density function. k cos for 0sxs1 f(x)=- for all other values of x (a) Show that k = Find p( x sxs). (b) (c) Find the median of X.arrow_forwardSolve itarrow_forward
- Let Y be a continuous random variable. Let c be a constant. PROVE Var (Y) = E (Y2) - E (Y)2arrow_forward3. Let X be a continuous random variable on the interval [0, 1] having cdf Fx(x) = 3x² − 2x³. Let W = 4 + 3X. (a) What is the range of W? (b) Find a formula for Fw(w). (c) Find a formula for fw(w).arrow_forwardSuppose that a > 0 is a constant. Let the joint pdf of random variables X,Y be fx,y (x, y) = a(x + y)e¬z-4, for all x > 0, y > 0. Find the conditional probability P (X < 1|Y < 2).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning
Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)TrigonometryISBN:9781337278461Author:Ron LarsonPublisher:Cengage Learning


Trigonometry (MindTap Course List)
Trigonometry
ISBN:9781337278461
Author:Ron Larson
Publisher:Cengage Learning