
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
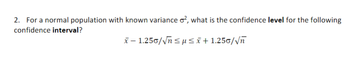
Transcribed Image Text:2. For a normal population with known variance o², what is the confidence level for the following
confidence interval?
x-1.250/√n≤µ ≤ x+1.250/√ñ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 9 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Find the F-test statistic to test the claim that the population variances are equal. Both distributions are normal. The standard deviation of the first sample is 3.96014.5373 is the standard deviation of the second sample.arrow_forwardAssume that we want to construct a confidence interval. Do one of the following, as appropriate: (a) find the critical value tα/2, (b) find the critical value zα/2, or (c) state that neither the normal distribution nor the t distribution applies. Here are summary statistics for randomly selected weights of newborn girls: n=282, x=32.1 hg, s=7.3 hg. The confidence level is 95%.arrow_forwardX. is found to be 19.1, and the A simple random sample of sizen is drawn from a population that is normally distributed. The sample mean, sample standard deviation, s, is found to be 4.9. (a) Construct a 96% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 39. (b) Construct a 96% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 68. How does increasing the sample size affect the margin of error, E? (c) Construct a 98% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 39. How does increasing the level of confidence affect the size of the margin of error, E? (d) If the sample size is 14, what conditions must be satisfied to compute the confidence interval? (a) Construct a 96% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 39. Lower bound: Upper bound: (Round to two decimal places as needed.) (b) Construct a 96% confidence interval about u if the sample size, n, is 68. Lower bound: ; Upper bound: (Round to two decimal places as needed.) How does increasing the sample…arrow_forward
- In a large scale study of energy conservation in single family homes, 20 homes were randomly selected from homes built in a housing development in southern England. Ten of the houses, randomly selected from the 20 houses selected for the study, were constructed with standard levels of insulation (70 mm of roof insulation and 50 mm of insulation in the walls). The other 10 houses were constructed with extra insulation (120 mm of roof insulation and 100 mm of insulation in the walls). Each house was heated with a gas furnace and energy consumption was monitored for eight years. The data shown below give annual gas consumption in MWh for each of the 20 houses. Standard Insulation Extra Insulation 13.8 15.1 17.8 13.9 18.0 15.9 17.3 17.2 16.9 15.2 19.9 13.8 13.6 11.3 17.6 13.2 15.9 18.8 12.3 14.0 Sample means Sample Standard Deviation 16.31 14.84 2.38 2.12arrow_forwardWhich alternative hypotheses will allow you to determine statistical significance at α = 0.05 using a 95% confidence interval? H a: μ = 30 H a: μ > 30 H a: μ ≠ 30 H a: μ <30arrow_forwardAn IQ test is designed so that the mean is 100 and the standard deviation is 10 for the population of normal adults. Find the sample size necessary to estimate the mean IQ score of statistics students such that it can be said with 99% confidence that the sample mean is within 4 IQ points of the true mean. Assume that σ=10 and determine the required sample size using technology. Then determine if this is a reasonable sample size for a real world calculation.arrow_forward
- Assume that we want to construct a confidence interval. Do one of the following, as appropriate: (a) find the critical value to/2. (b) find the critical value Zα/2, or (c) state that neither the normal distribution nor the t distribution applies. Here are summary statistics for randomly selected weights of newborn girls: n=218, x = 30.4 hg, s = 7.6 hg. The confidence level is 99%. ... Select the correct choice below and, if necessary, fill in the answer box to complete your choice. OA. ta/2= (Round to two decimal places as needed.) OB. Za/2 (Round to two decimal places as needed.) OC. Neither the normal distribution nor the t distribution applies.arrow_forwardIQ scores among the general population have a mean of 100 and a standard deviation of 14. A researcher claims that the standard deviation, o, of IQ scores for females is not equal to 14. A random sample of 24 IQ scores females had a mean of 98 and a standard deviation of 11. Assuming that IQ scores for females are approximately normally distributed, is there significant evidence (at the 0.05 level of significance) to conclude that the researcher's claim is correct? Perform a two-tailed test. Then complete the parts below. Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places and round your answers as specified below. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) (a) State the null hypothesis H, and the alternative hypothesis H,. H, :0 H, :0 (b) Determine the type of test statistic to use. (Choose one) ▼ O=0 OSO (c) Find the value of the test statistic. (Round to three or more decimal places.) Oarrow_forwardConstruct a 99% confidence interval for u, - H, with the sample statistics for mean cholesterol content of a hamburger from two fast food chains and confidence interval construction formula below. Assume the populations are approximately normal with unequal variances Stats X, = 98 mg, s,= 3.81 mg, n, = 14 x = 65 mg, s, =222 mg, n, =20 Confidence interval when variances are not equal +t. n2 d.f. is the smaller of n, - 1 or n, - 1 Enter the endpoints of the intervalarrow_forward
- IID Suppose X1, ..., X, N(u, o?). Construct a 95% confidence interval for o? when u is known.arrow_forwardAssume all populations are normally distributed. A travel analyst claims that the mean price of a round trip flight from New York City to Los Angeles is less than $507. In a random sample of 55 round trip flights from NYC to LA, the mean price is $502. Assume the population standard deviation is $111. At α = 0.05, is there enough evidence to support the travel analyst’s claim?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman