
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781305081550
Author: Braja M. Das
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I need detailed explanation solving this exercise from Foundation Engineering, step by step please.
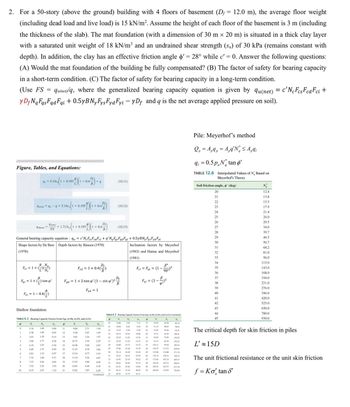
Transcribed Image Text:2. For a 50-story (above the ground) building with 4 floors of basement (D = 12.0 m), the average floor weight
(including dead load and live load) is 15 kN/m². Assume the height of each floor of the basement is 3 m (including
the thickness of the slab). The mat foundation (with a dimension of 30 m x 20 m) is situated in a thick clay layer
with a saturated unit weight of 18 kN/m³ and an undrained shear strength (Su) of 30 kPa (remains constant with
depth). In addition, the clay has an effective friction angle o' = 28° while c' = 0. Answer the following questions:
(A) Would the mat foundation of the building be fully compensated? (B) The factor of safety for bearing capacity
in a short-term condition. (C) The factor of safety for bearing capacity in a long-term condition.
(Use FS = qu(net)/q, where the generalized bearing capacity equation is given by qu(net) = c'NcFcs Fcd Fci +
YDNqFqsFqa Fai + 0.5yB Ny Fys Fya Fyi - YDf and q is the net average applied pressure on soil).
Figure, Tables, and Equations:
qu5.14c 1+0.195-
52) (1+0.4%)+9
9.-5.14c14
5.14c. (1+0.195)(1 +0.4%)
Qu(net) qu-q= 5.14c, 1+ 0.195
Pile: Meyerhof's method
Q₁ = 4,9 = 4,q'N₁₁ ≤ A¸¶₁
q₁ = 0.5ptan o'
TABLE 12.6 Interpolated Values of N Based on
Meyerhof's Theory
(10.11)
B
Soil friction angle, ' (deg)
20
21
N₁₁
(10.12)
all(net)
Qu(net)
FS
= 1.713c,(1+0.195)(1 +0.4%)
(10.13)
B
26
27
28
General bearing capacity equation qu= c'NcFcs Fca Fci+q'NqFqsFqaFqi + 0.5yBNy Fys Fya Fyi
Shape factors by De Beer Depth factors by Hansen (1970)
(1970)
29
Inclination factors by Meyerhof
(1963) and Hanna and Meyerhof
(1981)
33
2222222222223
12.4
13.8
15.5
17.9
24
21.4
25
26.0
29.5
34.0
39.7
46.5
30
56.7
68.2
81.0
96.0
Fcs = 1+
B N
L-Ne
34
Во
115.0
Fcd = 1 +0.4()
Fci = Fqi = (1
900)2
35
143.0
36
168.0
B
=
Fas 1+) tan op'
Fqd = 1 + 2 tan op' (1 - sin p')² -
Df
37
194.0
Fyi = (1
-
B
38
231.0
B
Fys = 1-0.4(7)
Fyd = 1
39
276.0
40
346.0
41
420.0
42
525.0
Shallow foundation:
TABLE 6.2 Bearing Capacity Factors From Eqs. (6.30), (6.29), and (6.31)
43
650.0
TABLE 6.2 Bearing Capacity Factors From Eqs. (6.30), (6.29), and (6.31) (Continued)
44
780.0
45
930.0
$'
N₂
N
Ny
$'
N
No
N₁
$'
No
22
N₁
Ny
$'
No
Na
16.88
7.82
7.13
37
55.63
42.92
66.19
Ny
23
18.05
8.66
8.20
38
61.35
48.93
78.03
0
5.14
1.00
0.00
11
8.80
2.71
1.44
24
19.32
9.60
9.44
39
67.87
55.96
92.25
1
5.38
1.09
0.07
12
9.28
2.97
1.69
The critical depth for skin friction in piles
25
20.72
10.66
10.88
40
75.31
64.20
109.41
2
5.63
1.20
0.15
13
9.81
3.26
1.97
26
22.25
11.85
12.54
41
83.86
73.90
130.22
3
5.90
1.31
0.24
14
10.37
3.59
2.29
27
23.94
13.20
14.47
42
93.71
85.38
155.55
4
6.19
1.43
0.34
15
10.98
3.94
2.65
28
25.80
14.72
16.72
43
105.11
99.02
186.54
L'≈ 15D
5
6.49
1.57
0.45
16
11.63
29
4.34
27.86
16.44
19.34
44
118.37
115.31
224.64
3.06
30
30.14
18.40
22.40
45
133.88
134.88
271.76
6
6.81
1.72
0.57
17
12.34
4.77
3.53
31
32.67
20.63
25.99
46
152.10
158.51
330.35
7
7.16
1.88
0.71
18
13.10
5.26
4.07
32
35.49
23.18
30.22
47
173.64
187.21
403.67
The unit frictional resistance or the unit skin friction
8
7.53
2.06
0.86
19
13.93
5.80
4.68
33
38.64
26.09
35.19
48
199.26
222.31
496.01
9
7.92
2.25
1.03
20
14.83
6.40
5.39
34
42.16
29.44
41.06
49
229.93
265.51
613.16
10
8.35
2.47
1.22
21
15.82
7.07
6.20
35
46.12 33.30
48.03
50
266.89 319.07
762.89
(continued)
36
50.59
37.75
56.31
f = Ko tan 8'
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Consider a continuous foundation of width B = 1.4 m on a sand deposit with c = 0, = 38, and = 17.5 kN/m3. The foundation is subjected to an eccentrically inclined load (see Figure 6.33). Given: load eccentricity e = 0.15 m, Df = 1 m, and load inclination = 18. Estimate the failure load Qu(ei) per unit length of the foundation a. for a partially compensated type of loading [Eq. (6.89)] b. for a reinforced type of loading [Eq. (6.90)]arrow_forwardA 300 mm 450 mm plate was used in carrying out a plate loading test in a sand, during which the plate settled 5 mm under the applied pressure of 250 kN/m2. a. What is the coefficient of subgrade reaction for a 300 mm wide square plate? b. What would be the coefficient of subgrade reaction of a 2 m 3 m foundation?arrow_forwardA square column foundation has to carry a gross allowable load of 1805 kN (FS = 3). Given: Df = 1.5 m, =15.9 kN/m3, = 34, and c = 0. Use Terzaghis equation to determine the size of the foundation (B). Assume general shear failure.arrow_forward
- The soil profile at a site consists of 10 m of gravelly sand underlain by a soft clay layer. The water table lies 1 m below the ground level. The moist and saturated unit weights of the gravelly sand are 17.0 kN/m3 and 20.0 kN/m3, respectively. Due to some ongoing construction work, it is proposed to lower the water table to 3 m below the ground level. What will be the change in the effective stress on top of the soft clay layer?arrow_forwardThe soil profile at a site consists of 10 m of gravelly sand underlain by a soft clay layer. The water table lies 1 m below the ground level. The moist and saturated unit weights of the gravelly sand are 17.0 kN/m3 and 20.0 kN/m3, respectively. Due to some ongoing construction work, it is proposed to lower the water table to 3 m below the ground level. What will be the change in the effective stress on top of the soft clay layer?arrow_forwardA column foundation (Figure 16.23) is 3 m 2 m in plan. Given: Df = 1.5 m, =25, c = 70 kN/m2. Using Eq. (16.9) and FS = 3, determine the net allowable load [see Eq. (16.16)] the foundation could carry. FIG. 16.23arrow_forward
- A 2.0 m wide continuous foundation carries a wall load of 350 kN/m in a clayey soil where = 19.0 kN/m3, c = 5.0 kN/m2, and = 23. The foundation depth is 1.5 m. Determine the factor of safety of this foundation using Eq. (6.28).arrow_forwardA flexible circular footing of radius R carries a uniform pressure q. Find the depth (in terms of R) at which the vertical stress below the center is 20% of q.arrow_forwardFrom the plate load test (plate dimensions 1 ft × 1 ft) in the field, the coefficient of subgrade reaction of a sandy soil is determined to be 60 lb/in3. What will be the value of the coefficient of subgrade reaction on the same soil for a foundation with dimensions of 20 ft × 20 ft?arrow_forward
- Repeat Problem 16.13 with the following: Mat foundation: B = 8 m, L = 20 m, and Df = 2 m Clay: =0 and cu = 130 kN/m2 16.13 A mat foundation measuring 14 m 9 m has to be constructed on a saturated clay. For the clay, cu = 93 kN/m2 and =0. The depth, Df, for the mat foundation is 2 m. Determine the net ultimate bearing capacity.arrow_forwardRefer to Figure 5.2. Given: B = L = 1.75 m, Df = 1 m, H = 1.75 m, = 17 kN/m3, c = 0, and = 30. Using Eq. (5.6) and FS = 4, determine the gross allowable load the foundation can carry.arrow_forwardFor the mat in Problem 16.15, what will be the depth, Df, of the mat for FS = 3 against bearing capacity failure? 16.15 Consider a mat foundation with dimensions of 18 m 12 m. The combined dead and live load on the mat is 44.5 MN. The mat is to be placed on a clay with cu = 40.7 kN/m2 and = 17.6 kN/m3. Find the depth, Df, of the mat for a fully compensated foundation.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305081550Author:Braja M. DasPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305635180Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781305970939Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled SobhanPublisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305081550
Author:Braja M. Das
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305635180
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Geotechnical Engineering (MindTap C...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305970939
Author:Braja M. Das, Khaled Sobhan
Publisher:Cengage Learning