
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
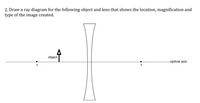
Transcribed Image Text:2. Draw a ray diagram for the following object and lens that shows the location, magnification and
type of the image created.
object
-optical axis
f
f
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A doctor examines a mole on the patient with a 17.2 cm focal length magnifying glass held 11.2 cm from the mole. Describe the image the doctor sees. A.Real B. Virtual C. Inverted D. Upright E. Smaller than object F. Larger than objectarrow_forwardThe angular magnification of a refracting telescope is 14. If the focal length of the objective lens is 70 cm, what is the distance between the object lens and the eyepiece? a. 95 cm b. 75 cm c. 90 cm d. 85 cm e. 80 cmarrow_forward1. If a lens is to focus parallel light rays on a screen 50-cm away, what diopter would it have? Explain.arrow_forward
- Which of the following statements is not consistent with geometric optics. a. Light rays propagate at small angles relative to the optical axis. b. The diffraction of light is neglected. c. Light rays propagate in straight lines. d. Light rays propagate near the optical axis. e. Ordinary objects always exhibit specular reflection when exposed to light.arrow_forwardWhich of the following scenarios does NOT result in refraction? a. The light must enter the medium parallel to the normal. b. Both the incident and refracting media must be transparent. C. The light must enter the medium at an angle > 0° with respect to the normal. d. Both substances must have different indices of refractionarrow_forward1. A beam of light emitted in air strikes the surface of mineral oil at the angle of 40 degreeswith respect to the normal line to the surface. Speed of light in air is 3 x 10^8 m/s in oil light travels with speed of 2.17x10^8 m/s. What is the angle of refraction? Draw the ray diagram.arrow_forward
- An object is 8.5 cm away from a thin convex lens with focal length of f1 = 3.1 cm. 8.0 cm away from the first convex lens is a second convex lens on the same optical axis with focal length of f2 = 2.1 cm. a) Draw a principal ray diagram for the optical system including the different focal lengths, image and object distances. b) Describe the nature (real or virtual) and orientation of the final image relative to the object. c) Calculate the position of the final image after the two lenses and its magnification.arrow_forwardprovide justificationarrow_forward4. Below is a diagram of an object arrow positioned such that it is bisected by the optical axis of an optical device whose focal point is as labelled. If an image of this object is viewed from the right of the optical device after the light has been affected by it, at which of the points indicated will the image of the point of the arrow be located? object a. A b. B c. C d. D e. It depends upon whether the optical device is a lens or a mirror.arrow_forward
- Which of the following is not a problem for refracting telescopes? O A. Different wavelengths of light are focused at slightly different locations. O B. The quality of the glass lens in transparency and in the shape of both surfaces must be high. C. The secondary mirror blocks some of the light passing through the primary lens. D. The primary lens can only be supported at the edges making deformation of large lenses difficult to avoid.arrow_forward4. An object is 2 meters from a thin lens with a focal length of 50 cm. Apply the thin-lens equation to calculate the image distance from the lens and magnification.arrow_forward3. Show that the magnification factor for a mirror or lens M = d/d do sign convention omitted) is the lateral magnification, or the ratio of the height (lateral size) of the image to that of the object. (Draw a ray diagram)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON