
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
My answer is incorrect, please write your explanation(process detail) why the answer is PV and write why my answer is wrong.
I attach the image and write my process of explanation.
My solution:
When the observer is moving away with a speed of vo.
Using Doppler's effect for this case,
f=fov-vov
Then observer speed will be
vo=v1-ffo
putting the values
vo=v1-pfofovo=v1-p
Hence, the speed of the observer (moving away) is vo=v1-p.
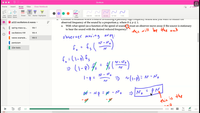
Professor's solution and answer (I attach in the image)

Transcribed Image Text:2. Consider a situation where a source is emitting a painfully high frequency sound and you want to reduce the
observed frequency of the sound by a proportion p, where 0 < p < 1.
With what speed (as a function of the speed of sound, v) must an observer move away if the source is stationary
to hear the sound with the desired reduced frequency?
a.
using 2oppler's efeet for this lase
1-६, ()
Then observer speed willbe
Vo= V()-?)
%3D
the speed of
the observer ( moving anoy)
a) v, =
Transcribed Image Text:OneNote
Home
Insert
Draw
View
Class Notebook
2 Share
Text Lasso Insert
Eraser
Pen
Marker Highlighter
Ink
0.25 mm
0.35 mm
0.5 mm
0.7 mm
1 mm
Mode Select Space
Color
2.
CONSIUCI a StuaIOT WTICIt a SOUILC IS CMUTng a pamuuny IugIIcquticy 5ounu ana you waIm TO Tcuuct uit
observed frequency of the sound by a proportion p, where 0 <p< 1.
With what speed (as a function of the speed of sound must an observer move away if the source is stationary
to hear the sound with the desired reduced frequency?
IN
p222 oscillations & waves v
а.
spring-mass sy..
Wk 1
will be the unit
oscillations HW
Wk 4
observer moving away:
waves example...
Wk 5
pendulum
N-No
fo - f, ( )
22w tests
f, =(1-) fs
» (1-p) %= %( )
N - No
T-p=
af - Np = gt -
No
this is the
it
ーダ
1х
10
9:45
-23:06
CC
속도
품질
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- MY NOTES ASK YOUR TEACHER PRACTICE ANOTHER A pulsar is a type of rotating neutron star that emits a beam of electromagnetic radiation. Imagine a pulsar that is moving toward Earth at a speed of 856.500 km/s. It emits mostly radio waves with a wavelength (at the source) of 132.500 cm. What is the observed wavelength of this radiation on Earth? (Assume the Earth is stationary. Consider the speed of light c = 3.00000 × 108 m/s. Give your answer to at least six significant figures.) 4.0 133 What relationship describes the frequency of a wave for an observer that is moving relative to the source? What is the relationship between frequency and wavelength? cmarrow_forwardMy answer is incorrect, please write your explanation(process detail) why the answer is v(p)/(1-p) and write why my answer is wrong. I attach the image and write my process of explanation. My solution: When the source is moving away with a speed of vs. Using Doppler's effect for this case, f=fo(v/v+vs) Then the speed f source will be vs=(fo/f)-1v putting the values vs=(fo/pfo)-1v=1p-1v Hence, the speed of the source (moving away) is vs=1p-1v. Professor's solution and answer I attach in the image.arrow_forwardPlease explain the steps to find the answer, which equation you are using and why you are using it. Also a small reflection about the problem. Thanks.arrow_forward
- Be thorough to the fullest for explaining this.arrow_forwardSpace Ship A is approaching Earth from the left at a speed of 0.84c relative to earth. Space Ship B is approaching earth from the right at a speed of 0.32c relative to Earth. Space Ship A emits light of wavelength 730m as seen on board Space Ship A. When this light is observed by Space Ship B, what wavelength does Space Ship B observe (in nm)? Show all work and look at correct answersarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON