
Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
2nd Edition
ISBN: 9780618974122
Author: Andrei Straumanis
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
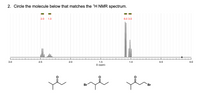
Transcribed Image Text:2. Circle the molecule below that matches the 'H NMR spectrum.
2.0
1.0
6.0 3.0
lle
3.0
2.5
2.0
1.5
1.0
0.5
0.0
Ō (ppm)
re
Br
Br
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Determine which of the following belongs to this ir spectra then complete the nmr analymethyl butanoate benzaldehyde 1-chlorobutane 1-chloro-2-methylpropane butan-2-one propan-2-ol propanalarrow_forwardCircle the molecule below that matches the 1H NMR spectrum. Please show work.arrow_forwardHi can you help me find the chemical reaction and molecular structure of this Nmr.arrow_forward
- analyze this H-NMR spectra of Vanillyl Alcohol. Results were gathered after a lab of synthesis of vanillyl Alcohol..arrow_forwarda) Make a table of the chemical shift, multiplicity and number of hydrogens for each 1H-NMR signal. b) Propose a structure consistent with the data and assign each proton in your structure to a signal in the NMR spectrum.arrow_forwardPlease give me the right answerarrow_forward
- In identifying the NMR regions, would the small round peak be classified as a singlet or doublet? Also, what is the key in identifying NMR regions (Multiplet, doublet etc.)arrow_forwardLooking at the NMR, how can you determine the compound is cyclohexane carboxaldehyde? Distinguish all the ppm (be detailed)arrow_forwardCAHOBR compound Which C,H,Br compound would give the following proton NMR spectrum? Enlargements of the signals are shown above each one. The integration is shown in a little box in the upper left. Chem shift 1.05 Rel area 0.00 1.97 1.00 3.31 2.00 TMS 3. 2. 0 ppm 4 6. Chemical shift (6) 10 c) 2-bromo-2-methylpropane d) 2-bromobutane 1-bromobutane b) 1-bromo-2-methylpropanearrow_forward
- Nonearrow_forwardDraw the structure for the H-NMR.arrow_forwardCan you explain spectroscopy? Let's start with NMR Spectroscopy. What is the difference between a proton being enantiotopic and homotopic? What does it mean for a proton to be shielded or deshielded? How do you determine J (the coupling constant)? What does 'coupling is mutual' mean? How is that translated on the NMS Spectroscopy spectrum? Does that have to do with the polarity of the molecule? Is there an easier way to explain that? When thinking about C-13 NRM Spectroscopy, what it meant by the statement, "the carbons cannot integrate"? When looking at an NMR Spectroscopy spectrum, how do you know which peak belongs to which proton? (The intensity of the peak and the ppm of the peak) P.S. These questions come from after watching a lecture. There is no graded assignment attached to these questions. I simply do not understand the material.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning
Organic Chemistry: A Guided InquiryChemistryISBN:9780618974122Author:Andrei StraumanisPublisher:Cengage Learning Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole
Macroscale and Microscale Organic ExperimentsChemistryISBN:9781305577190Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. MastersPublisher:Brooks Cole

Organic Chemistry: A Guided Inquiry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780618974122
Author:Andrei Straumanis
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Macroscale and Microscale Organic Experiments
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577190
Author:Kenneth L. Williamson, Katherine M. Masters
Publisher:Brooks Cole