
Calculus: Early Transcendentals
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781285741550
Author: James Stewart
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
match each of the following planar
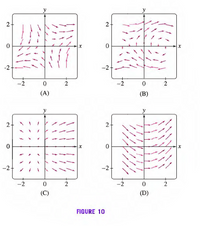
Transcribed Image Text:2-
2-
-2
-2+
2
-2
(A)
(B)
y
2+
-2-
-2-
-2
-2
2
(C)
(D)
FIGURE 10
2.
2.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, calculus and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Let L₁ be the line passing through the points Q₁(-4, 5, −5) and Q₂(−1, 6, −2) and let L2 be the line passing through the point P₁ (9, 11, 3) with direction vector d = [4, 2, 2] T. Determine whether L₁ and L₂ intersect. If so, find the point of intersection.arrow_forwardPlease give a full explanation to the answer and each of the steps.arrow_forward(1) Let x and y be the vectors x = and y = 4arrow_forward
- Which point has the gradient vector with the smallest magnitude? Barrow_forwardFind the vector equation of the line between the points (3, -1, 2) & (1, 4, -1), then graph the line. l(t) =arrow_forwardYou are on a rollercoaster, and the path of your body is modeled by a vector function r(t), where t is in seconds, the units of distance are in feet, and t = 0 represents the start of the ride. Assume the axes represent the standard cardinal directions and elevation (x is E/W, y is N/S, z is height). Explain what the following would represent physically, being as specific as possible. These are all common roller coaster shapes/behaviors and can be explained in specific language with regard to units: a. r(0)=r(120) b. For 0 ≤ t ≤ 30, N(t) = 0 c. r'(30) = 120 d. For 60 ≤ t ≤ 64, k(t) = 40 and z is constant. e. For 100 ≤ t ≤ 102, your B begins by pointing toward positive z, and does one full rotation in the normal (NB) plane while your T remains constant.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781285741550Author:James StewartPublisher:Cengage Learning Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON
Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134438986Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. WeirPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON
Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)CalculusISBN:9780134763644Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric SchulzPublisher:PEARSON Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Calculus: Early TranscendentalsCalculusISBN:9781319050740Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert FranzosaPublisher:W. H. Freeman
 Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Calculus: Early Transcendental FunctionsCalculusISBN:9781337552516Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. EdwardsPublisher:Cengage Learning

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781285741550
Author:James Stewart
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Thomas' Calculus (14th Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134438986
Author:Joel R. Hass, Christopher E. Heil, Maurice D. Weir
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals (3rd Edition)
Calculus
ISBN:9780134763644
Author:William L. Briggs, Lyle Cochran, Bernard Gillett, Eric Schulz
Publisher:PEARSON

Calculus: Early Transcendentals
Calculus
ISBN:9781319050740
Author:Jon Rogawski, Colin Adams, Robert Franzosa
Publisher:W. H. Freeman


Calculus: Early Transcendental Functions
Calculus
ISBN:9781337552516
Author:Ron Larson, Bruce H. Edwards
Publisher:Cengage Learning