Question
Need help
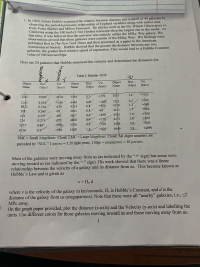
Transcribed Image Text:1929, Edwin Hubble examined the relation between distance and redshift of 46 galaxies by
Observing the period-luminosity relationship of Cepheid variables along with earlier data
Trom Vesto Slipher and Milton Humason. He did his work at the Mt. Wilson Observatory in
California using the 100 inch (2.5m) Hooker telescope-then the largest one in the world. At
that time, it was believed that the universe was entirely within the Milky Way galaxy. His
observations proved that these galaxies were outside of the Milky Way. His findings were
published first in The New York Times and then presented as a paper to the American
Astronomical Society. Hubble showed that the greater the distance between any two
galaxies, the greater their relative speed of separation. This would lead to a Hubble Constant
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios