Question
Vector Addition scale we can create our own for the graphic method
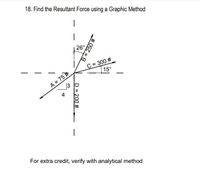
Transcribed Image Text:Title: Graphical Method for Finding the Resultant Force
Objective: Determine the resultant force using a graphical method.
Diagram Explanation:
The diagram illustrates four forces acting on a point in a plane, represented as vectors. Each vector has a specified magnitude and direction:
1. **Force A**:
- Magnitude: 75 pounds (#)
- Direction: Acts at an angle, forming a 3:4 slope with the horizontal.
2. **Force B**:
- Magnitude: 250 pounds (#)
- Direction: Oriented at an angle of 26 degrees from the vertical axis.
3. **Force C**:
- Magnitude: 300 pounds (#)
- Direction: Positioned at an angle of 15 degrees from the horizontal axis.
4. **Force D**:
- Magnitude: 200 pounds (#)
- Direction: Acts vertically downward.
Task:
- Use a graphic method to find the resultant of these four forces by vector addition.
- For additional practice, verify the resultant using an analytical method.
Note: The graphical method involves drawing each vector to scale on a grid and using head-to-tail addition to determine the resultant vector's magnitude and direction.
Extra Credit:
Verify your solution using an analytical method, such as resolving each vector into its rectangular components and applying vector addition principles.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1 Introduction
Force is a vector quantity which corresponds to the rate of change in momentum. It is also defined as the acceleration of a uniform mass object by Newton second law of motion.
The Resultant vector of numerous vectors corresponds to a vector which can replace those vectors without changing the effects. So, the resultant vector can be found using either graphical method or analytical method.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- a student begins her drive to school by traveling 14 miles in a direction of 45 degrees north of east. Next she travels 5 miles north. Finally, she travels 10 miles east when she arrives at school. a.) create a vector diagram showing the student’s path b.) determine the magnitude of the resultant vector c.) determine the direction of the resultant vector (0r) d.) determine the total distance drivenarrow_forwardWhen adding multiple two-dimensional displacement vectors, which of the following methods is most approp[riate to accurately determine the total displacement? 1. scale method diagram 2. Trigonometric method 3. magnitude adding method 4. algebriac component methodarrow_forwardHow to add vectors graphically? How to determine the resultant vector graphically?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios