
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Consider the beam with an overhang shown in the figure.
a. Determine the shear force V and bending moment M at a cross section located 18 ft from the left-hand end A.
- Find the required magnitude of load intensity q acting on the right half of member SC that will result in a zero shear force on the cross section IS ft from A.
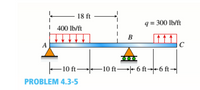
Transcribed Image Text:18 ft
q = 300 lb/ft
| 400 lb/ft
B
A
F10 ft -10 ft→- 6 ft→f-6 ft→
PROBLEM 4.3-5
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, civil-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A simple wooden AB beam (see figure 2) supportsa uniform load of 24 kN / m (includes weightcharacteristic of the beam), with a length L = 1.75m and sectionrectangular cross section with width of 200mm and height250mm. Determine:a) Reactions and shear diagram.b) Using the maximum shear force, find theshear stress in:to. The centroid.b. At a distance of 62.5mm from the centroid.c. At the ends of the cross section.c) Draw the shear stress diagram withall values obtained.arrow_forwardTwo vertical forces are applied to a simply supported beam with the cross-section shown. If L1-1 m, L2 = 3 m, and P = 18 kN, determine the maximum tension bending stress in the beam. The beam's moment of inertia about the z axis is 10,577,574 mm“, and the centroid of the section is located 139.1 mm above the bottom surface of the beam. 200 mm P P 15 mm 160 mm L1 L2 9 mm O 236.7 MPa O 152.0 MPa O 176.1 MPa O 280.4 MPa O 224.3 MPaarrow_forwardAC and BC have the same dimensions (a square cross section of 25 mm on each side)arrow_forward
- A pole is fixed at the base and is subjected to a linearly varying distributed force with maximum intensity of q and an axial compressive load P = 29 kips at the top (see figure). d₁ 10 ft 90=400 lb/ft The pole has a circular cross section with an outer diameter of 6.0 in. and an inner diameter of 5.5 in. Find the normal stresses on the surface of the pole at the base at locations A and B. (Assume that the bending moment is not affected by the presence of lateral deflections. Enter your answers in ksi. Use the statics sign convention. Assume that the +x-axis is to the right.) σ, ksi OF ksi d₂arrow_forwardProb.2 Determine (a) the maximum bending stress, (b) the maximum shearing stress due to V in the simply supported beam shown in the figure and (c) the shearing stress at a point 1m from the right support and 2 cm below the top. 40 kN/m 5 сm 16 kN m 16 cm - 1m- - 2 m - 2 m-arrow_forwardA cantilever beam of rectangular cross section is subjected to a concentrated load P = 150 kN acting at the free end (see Figure 1). The beam has width b = 80 mm. and height h = 260 mm. Point A is located at distance c = 0.5 m from the free end and distance d = 220 mm. from the bottom of the beam. a) Using Mohr's circle, calculate the principal stresses oơi and oz and the maximum shear stress Tmax at point A. b) Show these stresses on sketches of properly oriented elements. P b. Figure 1: A cantilever beamarrow_forward
- H.W.1 /The cantilever beam in Figure below has a rectangular cross section with dimension (20 mm(width) x40 mm (height)).(a). Find the maximum bending stress (oms) in the beam. (b) Find the maximum bending stress (amar) in point B and C in the beam (c)Sketch the bending stress distribution over the cross scction on which the maximum bending stress occurs. A в 10 Ib/ft C 20 ft 60 ftarrow_forwardProblem 5 Knowing that the ultimate stress at points A, B and D are 30 MPa, 155 MPa and 140 MPa respectively, what is the maximum allowable couple M that can be applied onto the beam of the shown cross section forming an angle B with the vertical plane. B = 15° B M S0 mm 20 mm s0 mm 30 mmarrow_forwardA simply supported beam is subjected to a linearly varying distributed load q(x) = qo with maximum intensity 9, at B. The beam has a length L = 4 m and rectangular cross section with a width of 220 mm and height of 285 mm. %3D 90 9(x) Determine the maximum permissible value for the maximum intensity, go, (in kN/m) if the allowable normal stresses in tension and compression are 130 MPa. kN/marrow_forward
- A simple beam of wide-flange cross section supports a uniform load of intensity q = 45 kN/m on a span of length L = 3 m. The dimensions of the cross section are h = 270 mm, b = 180 mm, and tf = 15 mm, tw = 12 mm, d = 0.8 m, and a = 60 mm. (a) Calculate the maximum shear stress omax on cross section A-A located at distance d = 0.6 m from the end of the beam. (b) Calculate the shear stress oB at point B on the cross section. Point B is located at a distance a = 60 mm from the edge of the lower flange. 2 2 A+ h 2 Вarrow_forwardThe overhanging beam ABC in Figure supports a concentrated load and a uniformly distributed load. The beam has a rectangle cross-sectional area of 120 mm × 180 mm (base x height). Neglect the weight of the beam. a) Construct the shear-force and bending-moment diagram. b) Determine the maximum normal stress in the beam and its location measured from point A. Ans : omax 173.92 MPa 20 kN 12 kN/m A B 4 m 10 m 20arrow_forwardThe cantilever beam is subjected to a concentrated load P. The cross-sectional dimensions of the rectangular tube shape are shown in the second figure. Assume b = 133 mm, d = 207 mm, y = 62 mm, yk = 37 mm and t = 6 mm. (a) Compute the value of Q that is associated with point H, which is located 62 mm above the centroid of the rectangular tube shape. (b) If the allowable shear stress for the rectangular tube shape is 117 MPa, determine the maximum concentrated load P that can be applied to the cantilever beam. Answers: (a) Q = (b) P = i i P Z mm³. kN. ун Ук H K b t (typ.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning