
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
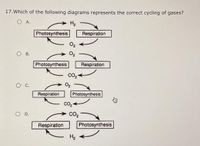
Transcribed Image Text:17.Which of the following diagrams represents the correct cycling of gases?
O A.
H2
Photosynthesis
Respiration
O2
В.
O2
Photosynthesis
Respiration
.
O2
Respiration
Photosynthesis
CO2
O D.
CO2
Respiration
Photosynthesis
H2
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 3arrow_forward1.The shorter the wavelength of visible light the Group of answer choices a, more photons it contains b, less energy absorbed by photosynthetic pigments c, reener the color d, greater the energy 2. The reason we breathe in oxygen is to assist in the production of Group of answer choices a, cell structures b, ATP c, Glucose d, Nitrogen 3. Why does a plant use the CAM or C4 pathway during photosynthesis? Group of answer choices a, To bind carbon dioxide and not use the C3 pathway in photosynthesis b, To bind Carbon dioxide to use later in the C3 pathway when carbon dioxide levels are low due to closed stomata c, Plants that use C4 and CAM do not do photosynthesis d, To use in the process of cell respiration when stomata are closedarrow_forwardWhich of the following pathways will split water and produce oxygen Select one: a. Gluconeogenesis b. Photosystem II c. Calvin Cycle d. Photosystem I e. Rubiscoarrow_forward
- A. Highlight all the organisms that CAN do photosynthesis (you might need to google search what these are) Venus fly trap Mycorrhizal fungus Cyanobacteria Red algae Sponges Corn (Zea mays) B. Summarize the purpose of photosynthesis______ C. How could you tell or measure the rate of photosynthesis? ____ D. What is a redox reaction? ___ E. When the water molecule donates its electron to the chlorophyll molecule the water molecule was ______ while the chlorophyll was ______. F. When the carbon chain gains electrons from NADPH the carbon chain has been _____. G. Discuss how the chloroplast structure is arranged using the following terms (include picture too) chloroplast, thylakoid, stroma, chlorophyll, H. Light reaction and Calvin cycle: what is the overall purpose of each one?arrow_forward10arrow_forwardPHOTOSYNTHESIS consists of . A. saptures D. light reactions in which energized B. stores it in C. in which electrons CO, fixed to RuBp and pass down then O2 evolved reduce NADP* to reduced and phosphorylated electron transport chain by mechanism of E. -using chemiosmosis rearranged to F. Ho generates release G3P regenerate G. in process called using made into glucose and other carbohydratesarrow_forward
- 1. Compare cellular respiration and photosynthesis. Which processes or structures are used in both in order to generate ATP? Select all that applay A. Chemiosmosis B. Substrate level phosphorylation C. Splitting of water to generate electrons D. An electron transport chain E. ATP synthasearrow_forwardDuring photosynthesis in chloroplasts, 02 is produced from reactions associated with via a series of O a. H2O PSII Ob. CO2 PSII O c. NADPH ATP synthase O d. H20 PSI О е. СО2 Calvin cycle Clear my choicearrow_forward54)arrow_forward
- 18. Cyanobacteria, green plants, and green algae generate exactly how many product molecules in their consumption of six CO.molecules and twelve H,O molecules during oxygenic photosynthesis? A. one C,H12O6 molecule, six H,O molecules, and six O, molecules are produced B. twelve C,H1,0, molecules, six H,O molecules, and three CO, molecules are produced C. six H,O molecules and twelve CO, molecules are produced D. six C,H1,0, molecules, three H,O molecules, and six CO, molecules are produced E. twelve H,O molecules and six O, molecules are producedarrow_forward13. Describe the differences between photosynthesis and cellular respiration in terms of redox chemistry.arrow_forward5arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education