
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:0.08 01 substrate?
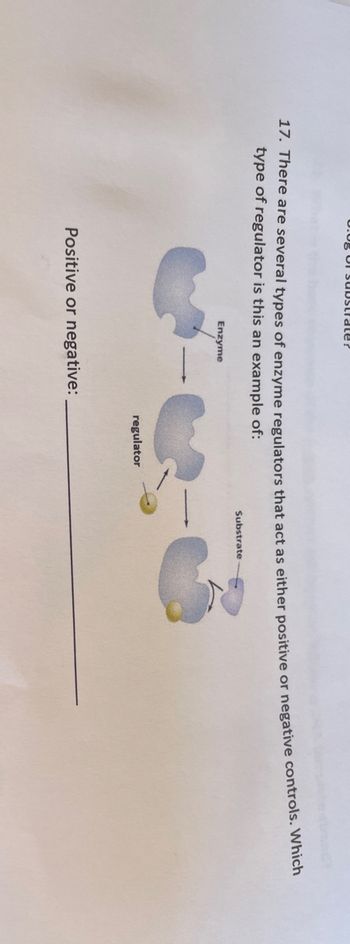
17. There are several types of enzyme regulators that act as either positive or negative controls. Which
type of regulator is this an example of:
Enzyme
Positive or negative:
regulator
Substrate
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Why do you think both enzymes tested have the exact same optimal working temperature (i.e. temperature they work best at)?arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwriting solutionarrow_forwardWhich inhibitor does the statement describe: 1. The structure of the inhibitor is similar to that of the substrate. Competitive Inhibitor or Noncompetitive Inhibitor 2. Adding more substrate to the reaction restores the enzyme activity. Competitive Inhibitor or Noncompetitive Inhibitorarrow_forward
- help with question 5 pleasearrow_forwardPredict the substrate and the activity (function) for a and b. For c and d, indicate the type of activity (class of enzyme) only. a) Maltase = b) Alcohol dehydrogenase c) CO2 H2C C. CH3 H3C H- H-N- CH- H,O H,N CH- OH CH CH, d) H,N CH OHarrow_forwardBriefly describe the major difference between the "lock and key" enzyme model and the "induced fit" enzyme model.arrow_forward
- According to the following graph, the activity of the enzyme decreases more sharply at high temperature than at low temperature. What are the reasons for this observation? Enzyme activity Optimum temperature Temperature, °C I. As temperature is increased, the substrate binding slowly becomes poorer. II. As temperature is decreased, the enzyme moves more slowly and so reacts more slowly. III. At higher temperatures, the enzyme is denatured and stops working entirely. IV. Temperature has no effect on enzyme activity. ○ I only O IV only I and III O II and IIIarrow_forwardHow does the metal ion in carboxypeptidase A increase the enzyme’s catalytic activitarrow_forwardQuestions #58 and #59 pleasearrow_forward
- Show chemical structures for treatment and their mechanism of action for a defective enzyme: Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase.arrow_forwardThe following graph is showing the effect of catalyzed reaction. Rate of reaction A enzyme concentration substrate concentration pH temperature B on the rate of an enzymearrow_forwardThe lock and key model and the induced fit model are two models of enzyme action explaining both the specificity and the catalytic activity of enzymes. Indicate whether each statement is part of the lock and key model, the induced fit model, or is common to both models. Lock and key model Induced fit model Common to both models Answer Bank The substrate binds to the enzyme at the active site, forming an enzyme-substrate complex. The substrate binds to the enzyme through noncovalent interactions. The enzyme conformation changes when it binds the substrate so that the active site fits the substrate. The enzyme active site has a rigid structure complementary to that of the substrate.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY