
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
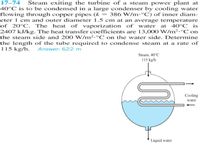
Transcribed Image Text:17–74 Steam exiting the turbine of a steam power plant at
40°C is to be condensed in a large condenser by cooling water
flowing through copper pipes (k == 386 W/m•°C) of inner diam-
eter 1 cm and outer diameter 1.5 cm at an average temperature
of 20°C. The heat of vaporization of water at 40°C _is
2407 kJ/kg. The heat transfer coefficients are 13,000 W/m2.°C on
the steam side and 200 W/m2.°C on the water side. Determine
the length of the tube required to condense steam at a rate of
115 kg/h. Answer: 622 m
Steam, 40°C
115 kg/h
Cooling
water
Liquid water
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- manufacturer plans to use steel wire (ks = 25 Wm-1 K-1 ) in a household appliance. For safetyconsiderations, we would like an estimate of the smallest electric current that is required to melt the wire.The bare wire is exposed to 20°C air with convective heat transfer coefficient of 15 Wm-2 K-1 and hasdiameter of 2.0 mm and electrical resistance of 0.20 W/m (i.e., per meter of wire). Thermal energy isproduced within the wire at the rate I2 Re , where I is the electrical current through the wire and Re is thewire’s electrical resistance. I = 0.643 Solve the microscopic energy balance in the steel wire with a prescribed temperature Ts at the wiresurface, as well as the requirement that temperature be finite at the center of the wire, to find anexpression for the temperature at the center of the wire in terms of the surface temperature Ts . Use yourresult to estimate the electric current at which the wire begins to melt.arrow_forwardThe resistance wire of a heater is composed of nichrome (a nickel-chromium alloy), completely surrounded by a 1/8 in (k = 0.15 BTU / h ft ºF) layer of asbestos, and this in turn, surrounded by another layer of 1/8 in.thick stainless steel (k = 10 BTU / h ft ºF). If the core temperature of the wire is kept constant at 1000 F, the convective heat transfer coefficient is 3 BTU / hft ºF, and the ambient temperature is 70 ºF. Calculate: a) The heat flux delivered to the wire in BTU / h ft^2 b) The outside temperature of the wire in ºFarrow_forwardHeat transfer is of critical importance in various industrial applications, including manufacturing. During machining, both the cutting tool and the workpiece will be significantly heated by friction heating. The heating of the cutting tool will reduce the tool hardness and strength, deteriorate the cutting quality, and shorten the tool life. Therefore, it is essential to prevent the overheating of the cutting tool during machining. Coolants are an instrumental part of machining to help cool the tool and the workpiece, provide lubricant, flush away chips, and prevent corrosion. The task of this project is to design the coolant to maintain the maximum machine tool temperature below 100 °C during the side milling process. As shown in the figure below, the machine tool has a diameter of 10 mm (D) and a length of 5 cm. The tool material is M2 high speed tool steel (T11302) and the workpiece is aluminum 6061. The spindle speed (w) is 2000 RPM and the cutting speed (v) is 50 mm/min. The feed…arrow_forward
- 18-51 A long 35-cm-diameter cylindrical shaft made of stainless steel 304 (k = 14.9 W/mK, p = 7900 kg/m³; cp = 477 J/kg - K, and a = 3.95 x 10-6 m²/s) comes out of an oven at a uniform temperature of 500°C. The shaft is then allowed to cool slowly in a chamber at 150°C with an average convection heat transfer coefficient of h = 60W/m².K Determine the temperature at the center of the shaft 20 min after the start of the cooling process. Also, determine the heat transfer per unit length of the shaft during this time period. Solve this problem using the analytical one-term approximation method. Answers: 486°C, 22,270 kJarrow_forwardcan you please work it please pleasearrow_forwardA 30-cm-radius metallic sphere is having thermal conductivity of k = 100. overall density of W 7 mk p = 1500- kg m² and heat capacity of C₂ = 3000 The sphere is initially at a uniform temperature of kgk CO T₁ = 20°C and is dropped into boiling water at T = 90°C. The convective heat transfer coefficient is assumed to be only h = 50; W m²K Using lump model, compute the temperature of the sphere after t = 1200 seconds. In solving this problem, please use and show the following steps (do not use EES) 1. Compute the volume and surface area 2. Compute the characteristic length Lc = k p Cp h Lc 4. Compute the Biot number Bi k 5. Calculate the Fourier number Fo= (at)/Lc² 6. Calculate the excess temperature using 0 = exp(-Bi * Fo) T-Too 7. Compute the target temperature T using 0 = Ti-Too 3. Compute the diffusivity a = = the sphere Vol Vol As == 3 r³ and А¸ = 4πr²arrow_forward
- What regime favors heat transfer and why?Laminar, Turbulent or Transitionalarrow_forwardA 30 m long pipe with an external diameter of 75 mm is being used to convey steam at a rate of 1000 kg/h. The steam pressure is 198.53 kPa. The steam enters the pipe with a dryness fraction of 0.98 and must leave the other end of the pipe with a minimum dryness fraction of 0.95. Insulation with a thermal conductivity of 0.2 W/(m K) is available. Determine the minimum thickness of insulation necessary. * Indicates an advanced level of difficulty in solving. 400 CHAPTER 4 Heat Transfer in Food Processing The outside surface temperature of insulation is assumed to be 258C. Neglect the conductive resistance of the pipe material and assume no pressure drop across the pipearrow_forwardIt is proposed to cool oil in a counter-current, concentric tube heatexchanger composed of a thin-walled inner tube of 0.02 m diametercarrying oil and thin-walled, perfectly insulated outer tube of 0.05 mdiameter carrying water. The oil flow rate is 50.0 kg min-1 and it has to becooled from 90°C to 40°C using 60 kg min-1 water at 20°C. Calculate the heat load and the outlet water temperature.arrow_forward
- C heat and mass transfer problemarrow_forwardThe condenser of a large thermal power plant is a body-tube type heat exchanger consisting of a single body and 30000 pipes with two passes each. The pipes are thin-walled with an inner diameter of 25 mm, and steam condenses on the outer surfaces of the pipes with a convection coefficient of 11000 W / m2.K. The heat transfer required by the heat exchanger is 2000 MW, and it is provided by the flow of water through the pipes at a flow rate of 30000 kg / h. Water enters at 20 ° C, steam condenses at 50 ° C. Calculate the temperature of the cooling water leaving the condenser? Determine the required pipe length per pass? The properties of water at Tort = 300 K; Cp = 4180 j / kgK, μ = 855 × 10--6 Ns / m2, k = 0.613 W / mK, Pr = 5.83.arrow_forwardA heat recovery device involves transferring energy from the hot flue gases passing through an annular region to pressurized water flowing through the inner tube of the annulus. The inner tube has inner and outer diameters of 24 and 30 mm and is connected by 8 struts to an insulated outer tube of 45-mm diameter. Each strut is 3 mm thick and is integrally fabricated with the inner tube from carbon steel (k = 50 W/m-K). D₂ D₁,2 Dil ↓ Water 1=3 mm Gas h Consider conditions for which water at 300 K flows through the inner tube at 0.161 kg/s while flue gases at 800 K flow through the annulus, maintaining a convection coefficient of 100 W/m².K on both the struts and the outer surface of the inner tube. What is the rate of heat transfer per unit length of tube from gas to the water? Use the Dittus-Boelter equation to obtain the water-side convection coefficient. Determine the rate of heat transfer per unit length of tube from gas to the water, in W/m. 9 = i W/marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY