
Advanced Engineering Mathematics
10th Edition
ISBN: 9780470458365
Author: Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher: Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
I need help on this?
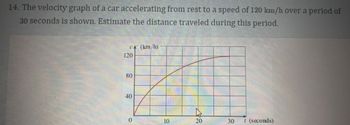
Transcribed Image Text:**14. The velocity graph of a car accelerating from rest to a speed of 120 km/h over a period of 30 seconds is shown. Estimate the distance traveled during this period.**
**Graph Description:**
- The graph depicts the velocity (v) of a car in kilometers per hour (km/h) over time (t) in seconds.
- The horizontal axis represents time, ranging from 0 to 30 seconds.
- The vertical axis represents velocity, ranging from 0 to 120 km/h.
- The curve starts at the origin (0,0), indicating the car is at rest initially.
- The curve gradually rises, indicating an increase in velocity, reaching 120 km/h at 30 seconds.
- The shape of the curve suggests a non-linear acceleration, possibly quadratic, due to its upward curvature.
**Estimation of Distance:**
To estimate the distance traveled, calculate the area under the velocity-time graph from 0 to 30 seconds. This area represents the total distance covered. The graph's shape suggests this area may be calculated using integration methods or approximated if a specific function is known.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 19 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated
Advanced Engineering MathematicsAdvanced MathISBN:9780470458365Author:Erwin KreyszigPublisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Numerical Methods for EngineersAdvanced MathISBN:9780073397924Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. CanalePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY
Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...Advanced MathISBN:9781118141809Author:Nathan KlingbeilPublisher:WILEY Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Mathematics For Machine TechnologyAdvanced MathISBN:9781337798310Author:Peterson, John.Publisher:Cengage Learning,


Advanced Engineering Mathematics
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780470458365
Author:Erwin Kreyszig
Publisher:Wiley, John & Sons, Incorporated

Numerical Methods for Engineers
Advanced Math
ISBN:9780073397924
Author:Steven C. Chapra Dr., Raymond P. Canale
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Introductory Mathematics for Engineering Applicat...
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781118141809
Author:Nathan Klingbeil
Publisher:WILEY

Mathematics For Machine Technology
Advanced Math
ISBN:9781337798310
Author:Peterson, John.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

