
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
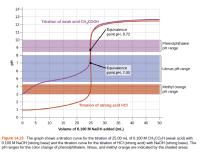
The titration curve as shown is for the titration of 25.00 mL of 0.100 M CH3CO2H with 0.100 M NaOH. The reaction can be represented as:
CH3 CO2 H + OH− ⟶ CH3 CO2− + H2 O
(a) What is the initial pH before any amount of the NaOH solution has been added? Ka = 1.8 × 10−5 for CH3CO2H.
(b) Find the pH after 25.00 mL of the NaOH solution have been added.
(c) Find the pH after 12.50 mL of the NaOH solution has been added.
(d) Find the pH after 37.50 mL of the NaOH solution has been added.
Transcribed Image Text:14-
13
Titration of weak acid CH,COOH
12
Equivalence
point pH, 8.72
10
Phenolphthalein
[pH range
Equivalence
point pH, 7.00
Litmus pH range
6.
Methyl orange
[pH range
4
3
Titration of strong acid HCI
1 -
10
15
20
25
30
35
40
45
50
Volume of 0.100 M NaOH added (mL)
Figure 14.23 The graph shows a titration curve for the titration of 25.00 mL of 0.100 M CH3CO,H (weak acid) with
0.100 M NaOH (strong base) and the titration curve for the titration of HCI (strong acid) with NaOH (strong base). The
pH ranges for the color change of phenolphthalein, litmus, and methyl orange are indicated by the shaded areas.
11
Hd
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 9 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 0.0415 L volume of 0.11 M hypochlorous acid (HCIO), a weak acid with K₂ = 4.0x108, is titrated with 0.11 M potassium a hydroxide (KOH), a strong base. Determine the pH at the following points in the titration. (a) before any KOH has been added с (b) after 0.0058 L KOH has been added Indicate which point is the equivalence point. O a b Od (c) after 0.0415 L KOH has been addedarrow_forwardA sample of acetic acid is titrated with a standardized NAOH solution. Before the end-point of the titration, which of the following must be true? HC,H3O, (aq) + NAOH (aq) → NaC,H3O2 (aq) + H2O (1) Note: [X] = molar concenctration of X %3D O [H+] > [OH-] [-HO] > [+H] O %3D [-HO] = [+H] Oarrow_forward1arrow_forward
- You are titrating 90.0 mL of a weak base solution (A-) with a concentration of 0.0515 M, using an HCl solution with a concentration of 0.0662 M. Note that the Ka Value for the conjugate acid , HA, is 5.6 x 10-10 . a) What is the pH of the initial weak base solution? b) What is the pH of the solution at the equivalence point? c) What is the pH of the solution when an additional 10 mL of HCl solution is added after reaching the equivalence point?arrow_forwardAspirin (C 9H 8O 4) is a weak monoprotic acid (K a = 3.3 x 10-4). You are analyzing a samplefor a pharmaceutical company with a quantitative titration and dissolve 10 tablets, eachcontaining 200 mg of aspirin, in 150 mL of water.a) Determine the pH of this solution.b) Determine the pH of the solution after you have added 20.0 mL of 0.500 M NaOH.arrow_forwardA buffer solution is made that is 0.417 M in HC1O and 0.417 M in KC1O. If K, for HC1O is 3.50 × 10-8, what is the pH of the buffer solution? PH = Write the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when 0.110 mol HNO3 is added to 1.00L of the buffer solution. (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Omit states of matter. Use H30* instead of H*)arrow_forward
- A 200mL solution of 0.3 M weak acid is titrated with 40 mL of 1.5 M NaOH. If the Ka of the acid is 5.37 x 10-10, what is the pH at this point in the titration?arrow_forwardNear the equivalence point in the titration of a strong acid with a strong base, one drop of base can cause the pH of the solution in the flask to change from 6.0 to 8.0. What is the relationship between the hydrogen ion concentrations at the two pH values? (A) The [H+] would be 100 times higher at pH 8.0 than 6.0. (B) The [H+] would be 200 times higher at pH 6.0 than 8.0. (C) The [H+] would be 2 times higher at pH 6.0 than 8.0. (D) The [H+] would be 2 times higher at pH 8.0 than 6.0. (E) The [H+] would be 100 times higher at pH 6.0 than 8.0.arrow_forwardYou have 25.00 mL of a 0.100 M aqueous solution of the weak base (CH3)2NH (Kb = 7.40 x 10-4). This solution will be titrated with 0.100 M HCl. (a) How many mL of acid must be added to reach the equivalence point? (b) What is the pH of the solution before any acid is added? ( c) What is the pH of the solution after 10.00 mL of acid has been added? (d) What is the pH of the solution at the equivalence point of the titration? (e) What is the pH of the solution when 30.00 mL of acid has been added?arrow_forward
- Calculate the pH of a buffer solution that contains 0.25 M benzoic acid (C6H5CO2H) and 0.15 M sodium benzoate (C6H5COONa). (K₂ = 6.5 × 10-5 for benzoic acid) aarrow_forwardIn a lab, you titrate 27.0 mL of 0.100 M acetic acid (CH3COOH, a weak acid, pKa 5.756, Ka 2.75 x 10-5), with 0.100 M NaOH. At the equivalence point, the concentration of the primary species in solution is approximately What is the pH of the solution at the equivalence point? At the equivalence point, what percentage of the analyte has been titrated?arrow_forwardA buffer solution is made that is 0.339 M in HF and 0.339 M in KF. If K, for HF is 7.20 × 10-4, what is the pH of the buffer solution? pH =| Write the net ionic equation for the reaction that occurs when 0.088 mol NaOH is added to 1.00 L of the buffer solution. (Use the lowest possible coefficients. Omit states of matter.) +arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY