
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
The bar is pin connected at B and is supported by rollers at C. Neglecting the weight of the bar, determine all reactions.
Please show a detailed and complete solution. Draw also a FREE BODY DIAGRAM.
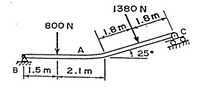
Transcribed Image Text:1380 N
800 N
1.8m1.8m
A
T 25°
B L1.5 m |
2.1 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Determine the components of reaction at E.arrow_forwardC 1.5 m B 950 Nm 0.7 m 50 mm A The rod shown above is composed of two connected segments: AB is steel with shear modulus Gsteel = 75 GPa and BC is brass with shear modulus Grass = 40 GPa. The steel segment has a diameter of 50 mm. a) Determine the required diameter of the brass segment such that the reaction at A will equal the reaction at C under the applied torque of 950 Nm at B. b) What is the magnitude and direction of the reactions at A and C? c) What is the maximum shear stress developed in the steel and brass rods d) What is the angle of twist at B relative to C?arrow_forwardВ A B C The system above is comprised of two-force members AB and AC, supporting a vertical force at point A. Assuming the system is drawn to scale and is in equilibrium, which of the following best describes the nature of the forces in members AB and AC? a) AB is in tension AC is in compression b) AB is in compression AC is in compression c) AB is in tension AC is in tension d) AB is in compression AC is in tensionarrow_forward
- F2 F1 a -2 m- -2 m- -2 m E 1.5 m F3 G 1.5 m F4 1.5 m Determine the reaction at support F and the force in members ED, EH, and GH of the truss. Tension is positive and compression is negative. Use F1 = 130 kN, F2 = 5 kN, F3 = 75 kN, and F4 = 220 kN for your calculations. You are encouraged to use the method of sections for determining the forces in the three members. The magnitude of the vertical reaction force at support F in kN (round to one decimal place): kN The force in member DE in kN (round to one decimal place): kN The force in member GH in kN (round to one decimal place): kN The force in member EH in kN (round to one decimal place): kNarrow_forwardfirst 3 parts pleasearrow_forwardQuestion 22 Consider the structure below, the components of the reaction force at C are Cx = _N. +m 22 لتر - N and Cy= - 3marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning