
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
I don't get it at all. I struggled with my homework. Can you help me about the Henderson-Hasselbalch relation, summarized in the table below, it is possible to predict the predominant form of these groups at a particular pH? Draw the line bond structure for the general form of an amino acid using "R" to represent the side chain. Draw the N- and C-terminus groups using the forms that are predominant at physiological pH (pH = 7.4. Include lone pairs in your drawing.
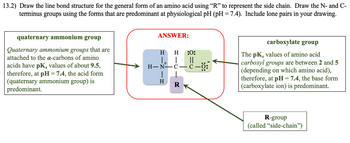
Transcribed Image Text:13.2) Draw the line bond structure for the general form of an amino acid using “R” to represent the side chain. Draw the N- and C-
terminus groups using the forms that are predominant at physiological pH (pH = 7.4). Include lone pairs in your drawing.
quaternary ammonium group
Quaternary ammonium groups that are
attached to the a-carbons of amino
acids have pK₂ values of about 9.5,
therefore, at pH = 7.4, the acid form
(quaternary ammonium group) is
predominant.
ANSWER:
H :0:
||
H-N—C—C—0:
H
H
R
carboxylate group
The pKa values of amino acid
carboxyl groups are between 2 and 5
(depending on which amino acid),
therefore, at pH = 7.4, the base form
(carboxylate ion) is predominant.
R-group
(called "side-chain")
![Draw the line bond structure for the general form of an amino acid using "R" to represent the side chain. Draw the N- and C-
terminus groups using the forms that are predominant at physiological pH (pH = 7.4). Include lone pairs in your drawing.
HINT:
The structure of the predominant form of an amino acid will depend on the pH because amino acids
involve the carboxyl group/carboxylate group conjugate pair and the quaternary ammonium
group/amine group conjugate pair. Using the implications of the the Henderson-Hasselbalch
relation, summarized in the table below, it is possible to predict the predominant form of these
groups at a particular pH.
Solution
Condition
pH <pka
pH > pKa
pH = pka
Relative Amounts of
Acid and Base Forms
[HA] > [A-]
[A-] > [HA]
[HA] = [A-]
The pK₂ values of amino acid carboxyl groups are between 2 and 5 (depending on which amino
acid), therefore, at pH = 7.4, the base form (carboxylate ion) is predominant.
Quaternary ammonium groups that are attached to the a-carbons of amino acids have pk₁ values of
about 9.5, therefore, at pH = 7.4, the acid form (quaternary ammonium group) is predominant.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/3442c249-7c73-43ca-b651-caace2a5bb24/7b70351f-1657-451c-9025-3cfa72cb8d1e/pmikoqg_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:Draw the line bond structure for the general form of an amino acid using "R" to represent the side chain. Draw the N- and C-
terminus groups using the forms that are predominant at physiological pH (pH = 7.4). Include lone pairs in your drawing.
HINT:
The structure of the predominant form of an amino acid will depend on the pH because amino acids
involve the carboxyl group/carboxylate group conjugate pair and the quaternary ammonium
group/amine group conjugate pair. Using the implications of the the Henderson-Hasselbalch
relation, summarized in the table below, it is possible to predict the predominant form of these
groups at a particular pH.
Solution
Condition
pH <pka
pH > pKa
pH = pka
Relative Amounts of
Acid and Base Forms
[HA] > [A-]
[A-] > [HA]
[HA] = [A-]
The pK₂ values of amino acid carboxyl groups are between 2 and 5 (depending on which amino
acid), therefore, at pH = 7.4, the base form (carboxylate ion) is predominant.
Quaternary ammonium groups that are attached to the a-carbons of amino acids have pk₁ values of
about 9.5, therefore, at pH = 7.4, the acid form (quaternary ammonium group) is predominant.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Look at the amino acids shown below. Their side chains are highlighted, Which amino acids have polar side chains? *** H,N-Ç-COOH H,N- C-COOH COOH H,N-C-COOH CH2 CH, H. H-C-CH, NH3 ČH, H. H. OH Вarrow_forwardNow let us look at a real amino acid, alanine. Fill in the chart below for each ionizable group. You need only the relationship discussed in the pdf posted and the numbers posted below. The next 6 questions will ask for the numbers you calculated for each of the letters below. pH when Average charge of group Group Ka pKa [A]/[HA] = 1 when pH = pK alpha-COOH ~10-2 A C alpha-NH3* ~10-9 Вarrow_forwardConsider the hexapeptide S-H-I-R-M-P Draw the structure at pH 1.0. What is the charge at this point? Draw the structure at pH 7.4. What is the charge at this point? Determine the pl and draw its structure.arrow_forward
- Researchers discover a new amino acid. Its R-group exclusively has hydrogen and carbon atoms. What behavior will this amino acid show? O Relative to the amino acids found in organisms, its interactions with water will be very high. It is hydrophilic. Relative to the amino acids found in organisms, its interactions with water will be intermediate. It is hydrophobic.arrow_forwardIdentify the part of a generic amino acid that reacts with base and the part that reacts with acid. Briefly explain your answer.Hint: Draw Lewis structures for ammonia (NH 3) and acetic acid (CH 3COOH).arrow_forwardFor the amino acid alanine, the major species in solution at pH 7 is the zwitterionic form, which has a negatively charged carboxylic acid group and a positively charged amino group. There is a less common neutral form in which neither group is charged. The carboxylic acid group of alanine has a p?a of 3 The amino group of alanine has a p?a of 8 Estimate the ratio of the concentration of the neutral amino acid species to the zwitterionic species at pH 7. __?__x10^?arrow_forward
- Explain why casein precipitates when vinegar is added. Why was milk or raw egg once used as an antidote in cases of heavy metal poisoning? Based on your isolated yield of casein, how many grams of the protein are in one 200 g glass of milk? Which of the solutions contained amide bonds? Which test tells you this? Which of the solutions contained compounds with primary amino groups? Which test tells you this? Describe two examples of protein folding patterns and identify what level of protein structure they belong to. What other reagents might you use besides ferric chloride to test affinity for metal ions?arrow_forwardH N. NH3 'N' NH3 NH Part A What are the amino acids in kyotorphin? Spell out the full names of the compounds. Enter your answers separated by a comma. Submit Request Answer Part B How would you name the dipeptide in kyotorphin? Spell out the full name of the compound.arrow_forwardWhat do your findings suggest about the stability of proteins in the presence of organic solvents?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY