
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
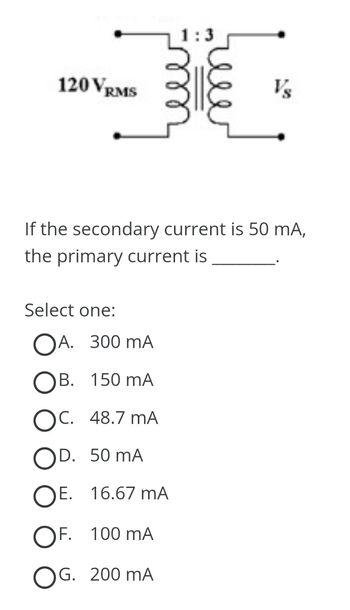
Transcribed Image Text:120 VRMS
1:3
Select one:
OA. 300 mA
OB. 150 mA
OC. 48.7 MA
OD. 50 mA
OE. 16.67 MA
OF. 100 mA
OG. 200 mA
weer
Vs
If the secondary current is 50 mA,
the primary current is
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The value of po in a silicon semiconductor at T = 300K is 6.0 X 1015 cm-³. Determine EF - Ev EF-Ev= 0.183 eV EF - Ev = 0.179 eV EF - Ev = 0.071 eV EF - Ev = 0.193 eVarrow_forwardLight-emitting diodes (LEDs) are diodes made with III-V compound semiconductor materials such as aluminum gallium arsenide (AlGaAs), aluminum indium gallium phosphide (AllnGaP) or indium gallium nitride (InGaN), instead of silicon. The LEDs emit light when the device is operated under forward bias. LEDs of different colors have different turn-on voltages VD(on). For example: Color VD(on) Red ~ 1.6 V Yellow ~ 1.7 V (a) Model these five LEDs with a simplified piecewise linear model. (b) A rule of thumb is that it takes about 1 mA of current to "light" an LED while~ 10 mA is needed for it to appear bright. Use the piecewise linear model for the LEDs, for the over-voltage indicator circuit to the right, find the values of Vin which will cause D₁ or D₂ to light (i.e. when ID1 or ID2 exceeds 1 mA). Green ~ 1.8 V Blue ~ 2.8 V loks o mu Vin Red LED Red LED White ~ 3.8 V + lov 21 D₁ D2 -10V o t Vout 오arrow_forwardFind values of the intrinsic carrier concentration ni for silocon at 0Carrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,