
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question

Transcribed Image Text:12 What is regenerated in the citric acid cycle?
13 During acetyl-CoA formation and the citric acid cycle, all of the carbons from glucose are released
as
14 Where does the electron transport chain occur in a cell?
15 What "waste" product of photosynthesis is used in electron transport chain? After the product, indicate
what its role is in aerobic respiration.
16 What is the role of the coenzymes (NADH & FADH;) in aerobic respiration?
17 Describe how ATP is formed (include the terms: electron transport chain, chemiosmosis, and ATP
synthase)?
18 How many ATPS are formed in electron transport chain and chemiosmosis?
a Theoretically, one NADH is used to produce
molecules of ATP.
b Theoretically, one FADH, is used to produce
molecules of ATP.
19 Consider fermentation.
a How many ATPS are formed?
By what process?
b What is the purpose of changing pyruvate into lactate or alcohol?
c When do our muscles produce lactate?
d Alcohol has one less carbon than pyruvate. What happens to the other carbon?
e How have we (humans) made use of alcohol fermentation?
20 Draw a diagram illustrating how different food sources can be used for energy (carbohydrates, proteins,
fats, etc.). Use this entire page. Include all of the following terms: acetyl CoA, amino acids, ATP, beta
oxidation, carbohydrates, citric acid cycle, citrate, CO,, deamination, electron transport chain, fats,
fatty acids, glucose, glycerol, H,0, NADH, NH,,O, oxaloacetate, proteins, pyruvate, urea. Note that
some of these terms are not in your textbook, but will be presented in lecture. For assistance, see:
http://chemistry.elmhurst.edu/vchembook/640reviewmetab.html
Transcribed Image Text:21 In cellular respiration, the oxidation of one molecule of glucose produces
ATP.
22 The oxidation of one 20 carbon fatty acid produces
ATP.
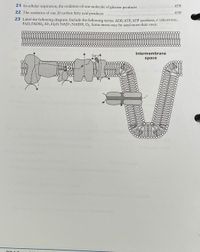
23 Label the following diagram. Include the following terms: ADP, ATP, ATP synthase, e (electrons),
FAD, FADH2, H*, H2O, NAD*, NADH, O2. Some terms may be used more than once.
Intermembrane
Cyt c4
space
femention
DIO a
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Per molecule of pyruvate, how many molecules of CO2 are produced during acetyl-CoA formation and the citric acid cycle (Stages 2 and 3)?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Per molecule of pyruvate, how many molecules of CO2 are produced during acetyl-CoA formation and the citric acid cycle (Stages 2 and 3)?
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- 2a. How many NADH are made during glycolysis from one glucose? 2b. How many NADH are made during the citric acid cycle from one glucose? 2c. How many FADH2 are made during the citric acid cycle from one glucose?arrow_forward8. Indicate the number of moles each of the molecules below formed from running three moles of glucose through glycolysis and Krebs cycle Moles produced from two moles of glucose running through Glycolysis Moles produced from two moles of glucose being oxidized in the PDC/Krebs Cycle Molecule Produced ATP GTP NADH + H* FADH2 CO2 D Focus United States) W DE DELL F11 F12 F8 F9 F10 F6 FZ (8)arrow_forward1. What stages of energy transformation occur after glycolysis in the presence of oxygen? Pyruvate oxidation and fermentation O Pyruvate oxidation, citric acid cycle, and fermentation Pyruvate oxidation, citric acid cycle, and electron transport/ATP synthesis All of the above 2. Which statement is most accurate? * Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon Carbon is more electronegative than oxygen Oxygen and carbon are equally electronegative All of the above 3. Reduction is the of electrons (or hydrogens, since they are so generous with their electrons). Oxidation is the ___________ of electrons (or hydrogens) gain; loss loss: gain gain; gain loss; lossarrow_forward
- 5. Which of the following pathways will use coenzyme A during aerobic cellular respiration? electron transport system pyruvate oxidation glycolysis Krebs cyclearrow_forward15. Why do we need oxygen? Group of answer choices It is the moleucle that gets added to CO2. It is the molecule that is required to make pyruvate. It is the molecule that drives the majority of ATP production.arrow_forwardIs this correct?arrow_forward
- 5. Explain how proteins produced in the rough endoplasmic reticulum can be secreted into the extracellular environment without ever crossing the plasma membrane. Use the terms rough endoplasmic reticulum, ribosome, lumen, Golgi apparatus, cell membrane in your answer. 6. Describe the major inputs and outputs of glycolysis, the citric acid cycle, and the electron transport system. oal 6a. List all the inputs and outputs of glycolysis and explain any assumptions you make. Inputs: Outputs: 6b. List all the inputs and outputs of the citric acid cycle and explain any assumptions you make. Outputs: Inputs: 6c. List all the inputs and outputs of the electron transport system and explain any assumptions you make. Inputs: Outputs: 6d. How are the high energy electrons captured from glycolysis and the citric acid cycle converted into ATP in mitochondria?arrow_forward10. Using either the Oxidative Phosphorylation stage of cellular respiration or the Cytochrome complex of photosynthesis, DIAGRAM AND EXPLAIN how electron transport chains function and are used to generate ATP in plants and animals. Make sure to supply sufficient detail to clearly convey your understanding of the process/mechanism.arrow_forward341arrow_forward
- 8arrow_forward32arrow_forwardQuestion 4: What serves as the final electron acceptor in the transport chain? Answer: Question 5: The 4-carbon molecule that is recycled during the citric acid cycle is: (pick one) oxalacetate ADP acetyl CoA RuBP Question 6. The enzyme used to synthesize ATP during chemiosmosis is known as Answer: Question 7: Most of the carbon dioxide produced by the catabolism of glucose is released during (pick one) the citric acid cycle the electron transport chain chemiosmosis glycolysis Question 8: The reduced form of NAD is: Answer: ***I do not need a feel explanation of the questions, just pick one if its multiple choice and fill in the black for the others please****arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education