
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
12
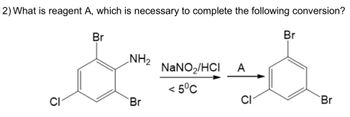
Transcribed Image Text:**Question 12:** What is reagent A, which is necessary to complete the following conversion?
**Chemical Conversion Details:**
- **Reactant Structure:** The starting compound is a benzene ring with three substituents: a bromine (Br) atom, an amino group (NH₂), and a chlorine (Cl) atom, arranged with the bromine and amino groups ortho to each other.
- **Reaction Conditions:** The reactant is treated with sodium nitrite (NaNO₂) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) at a temperature below 5°C.
- **Intermediate Reaction Step:** The reaction results in the formation of a diazonium salt intermediate, not shown, which requires further treatment with reagent A.
- **Product Structure:** The product structure is a benzene ring with bromine and chlorine atoms in the same positions as the original reactant, but the amino group is removed.
**Explanation of Conversion Process:**
1. **Formation of Diazonium Salt:** The initial step involves treating the amino-substituted benzene with NaNO₂ and HCl to form a diazonium ion intermediate.
2. **Role of Reagent A:** Reagent A is typically a reducing agent or a nucleophile that completes the conversion process by replacing the diazonium group.
3. **Final Product:** The final aromatic compound retains the original bromine and chlorine substituents, while the position formerly occupied by the amino group is now a hydrogen atom.
In this reaction, reagent A is likely hypophosphorous acid (H₃PO₂), which facilitates the conversion of the diazonium salt to the plain benzene ring by reducing the diazonium group.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- How did they get 3? Do you always have to divide?arrow_forwardis this right?arrow_forwardRx Paregoric 15.0 mL Pectin 0.5 g Kaolin 20.0 g Ethanol 1.0 mL Purified water ad 100.0 mL Mix and make a suspension Sig. 15 mL p.r.n. for diarrhea How many milligrams of kaolin are contained in each dose? Amount of kaolin in each dose = mgarrow_forward
- how do i find the freezing point of this graph?arrow_forwardP = P2O5 × 0.44 P2O5 = P × 2.29 K = K2O × 0.83 K2O = K × 1.21 1 tonne = 1,000 kg 1 ha = 10,000 m2 Using the conversions above calculate : 1.How much N and K are in a 25 kg bag of 12-22-18? 2. How much P2O5 and P are in a 20 kg bag of 0-46-0? 3. How much K2O and P2O5 are in a 35 kg bag of 12-22-18?arrow_forwardChemistry Cn.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY