
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
An object of mass 12 kg is suspended from a pulley which has a mass of 6 kg and a radius of rotation of 0.25 m. If at that time the pulley rotates with an angular velocity of 5 rad/s, we want to know that when the object moves down a distance of 2 m, then at what speed is the pulley rotating? If the friction force on the pulley bearing produces a moment of resistance of 2 N-m
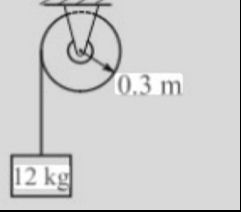
Transcribed Image Text:12 kg
0.3 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A student sits on a rotating stool holding two 3.0 kg objects. When his arms are extended horizontally, the objects are 1.0 m from the axis of rotation, and he rotates with an angular speed of 0.75 rad/s. The moment of inertia of the student plus stool is 3.0 kg•m and is assumed to be constant. The student then pulls the objects horizontally to 0.50 m from the rotation axis. (a) Find the new angular speed of the student. 1.907 Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. rad/s (b) Find the kinetic energy of the student system before and after the objects are pulled in. before afterarrow_forwardThe disk with a diameter of 20cm and a mass of 300g and the border of a disk-shaped object with a diameter of 30cm and a mass of 600g are interlocked. Apply a force of 9 N to the outer circumference of the small disk and rotate the two plates together. Find each torque applied to the small disk and the torque applied to the large disk.arrow_forwardTwo blocks with masses M1 and M2 are connected by a massless string that passes over a pulley as shown. M1 is on an incline of 49.5° with coefficient of kinetic friction μ1 = 0.205. M2 has a mass of 4.84 kg and is on an incline of 35.5° with coefficient of kinetic friction μ2 = 0.105. The pulley can be modeled as a disk with a mass of 305 g and radius of 15 cm. When the system is released, Block M2 accelerates down the incline at rate of 0.52 m/s2. (a) Determine mass of block 1 and the tension forces in the string connecting the blocks and the pulley. Draw accurate free body diagrams of both blocks and pulley, label each force correctly and show the steps in derivation of equations. (b) How much energy will be dissipated by friction 2 second after the blocks are released?arrow_forward
- A 0.32 lbm baseball is tethered to a string and swung by a rotating vertical pole. If the string is 12 ft long and the speed of the ball is 55 mph, determine the tension in the string, the angle the string makes with the vertical and the angular speed of the pole. ANS. 0=86.6°, T = 5.4 lbf, o=6.73 rad/secarrow_forwardA box of mass m = 0.7 kg is attached to a rope which is wrapped around a physical pulley with a radius of R = 10.2 cm and a rotational inertia of I = 0.075 kg·m2. When the box is released it starts to fall down with a constant acceleration and, at the same time, the pulley starts to spin up, see the picture below. Assuming that the pulley is frictionless, what is the magnitude of the box's acceleration and what is the tension in the rope? The acceleration of the box, a ? The tension in the rope, T? If the box starts from rest and traveled downwards a distance of h = 28 cm, what is the speed of the box and what is the angular velocity of the pulley? The speed of the box, v =? The angular velocity of the pulley, ω? -------------------------------------------------------------- A Merry Go Round carousel has a radius of R = 2.4 m and a rotational inertia of I = 695 kg·m2. A 75‑kg student is on the carousel at the midpoint between the carousel's center and the rim (at R/2 distance from…arrow_forwardConsider a uniform ladder of length 4.3 m and mass 10 kg. The ladder is falling over, pivoting about the end that is touching the ground. Someone is pushing on the top end of the ladder with a horizontal force of size 415 N. At the instant when the ladder makes a 46 degree angle with the horizontal, calculate the net torque on the ladder about its bottom end, in N m. Make your answer positive, and use g = 10 m/s2. (Please answer to the fourth decimal place - i.e 14.3225)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY