
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
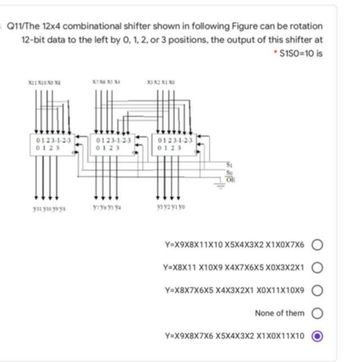
Transcribed Image Text:Q11/The 12x4 combinational shifter shown in following Figure can be rotation
12-bit data to the left by 0, 1, 2, or 3 positions, the output of this shifter at
*$150=10 is
X11X10 XD XI
0123-1-2-3
0123
yıl yio yoys
X7 X6 X5 X4
0123-1-2-3
0123
y1y6ys ya
X1 X2 X1 X3
0123-1-2-3
0123
узуг уг уо
So
OF
Y=X9X8X11X10 X5X4X3X2 X1X0X7X6 O
Y=X8X11 X10X9 X4X7X6X5 X0X3X2X1
Y=X8X7X6X5 X4X3X2X1 X0X11X10X9
None of them O
Y=X9X8X7X6 X5X4X3X2 X1X0X11X10
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- True or False Questionarrow_forwardA shunt generator supplies a 20kW load at 200V through cables of resistance, R= 100mΩ. If the field winding resistance, Rf =50Ω and the armature resistance, Ra =40mΩ, determine (a) the terminal voltage, and (b) the e.m.f. generated in the armaturearrow_forwardTrace the subtractor's logic when performing 2-5. а3 а2 а1 а0 b3 b2 b1 b0 а3 а2 а1 а0 b3 b2 b1 b0 cin 0 0 1 0 Ex: 0000 0/1 cout s3 s2 s1 s0 4-bit adder cout s3 s2 s1 s0 4-bit subtractorarrow_forward
- Assume that the system has eight 2-bit data inputs, A=a1a0, B=b1b0, C=c1c0, D=d1d0, W=w1w0, X=x1x0, Y=y1y0, Z=z1z0. There are also 2 control bits s1s0. The system computes A+B, C+D, W+X, and Y+Z when s1s0 equal to `11', `10', `01', `00', respectively. Use 1-bit 2-to-1 multiplexers and a 2- bit adder to implement this function. Please show how the inputs, multiplexers, and adder are connected. Label the inputs and select signals clearly. You don't need to show the details of the adder. (Hint: The adder has two 2-bit inputs E=e1e0 and F=f1f0. Each of E and F is generated by a 2-bit 4-to-1 multiplexer, which can be built using 1-bit 2-to-1 multiplexers.)arrow_forwardQ1. 12.11 Redesign the right-shift register circuit of Figure 12-10 using four D flip-flops with clock enable, four 2-to-1 MUXes, and a single OR gate. Qo 01 10 00 01 01 10 D O D O DQ 10 D. D D Do Sh 7. CLK 72°F Sunnyarrow_forward14--17) Given the unusual circuit below constructed of full and half adders, determine the 5 bit output of the circuit for each of the given 2 bit values for A and B. A, B, Ao Bo НА FA НА FA 14) A = 10 B = 11 16) A = 01 B = 10 15) A = 11 B = 10 17) A = 10 B = 01arrow_forward
- Design a circuit that displays the letters A through J on a seven-segment indicator. The circuit has four inputs W,X, Y, Z, which represent the last 4 bits of the ASCII code for the letter to be displayed. For example, if WXYZ =0001, "A" will be displayed.arrow_forward10. For the register shown below, if Do=1, D₁=0, D2=0, D3=1. After three clock pulses, what are the data outputs? Parallel data inputs CLK Do D₁ D₁ Dy D D D D Qo Q2 Parallel data outputsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,