
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Take note that the cross sectional area is 1.6 in2 and given in the figure is 36 kips
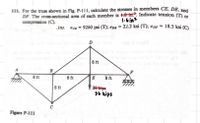
Transcribed Image Text:111. For the truss shown in Fig. P-111, calculate the stresses in members CE, DE, and
DF. The cross-sectional area of cach member is 1.8 in.. Indicate tension (T) or
compression (C).
1.6in2
.ins. OCE = 9260 psi (T); ODE = 22.2 ksi (T); O DF
18.5 ksi (C)
%3D
%3D
D
6 ft
B
F
8 ft
8 ft
8 ft
6 ft
30 kips
36 kips
C
Figure P-111
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- what is the answer on this problem number 105?arrow_forwardPROB. 1. For the truss shown in Fig. 1, Calculate the stresses in members CE, DE and DF. The cross-sectional area of each member is 1500 mm² A 2.0 M B с 1.5M 4⁰0 KN Fig. 1, 2.0 m E (1) IS M D 2.0 m 50 KN Farrow_forwardA double-decker train. EXERCISES 1. A reciprocating steam engine connecting rod is subjected to a maximum load of 65 kN. Find the diameter of the connecting rod at its thinnest part, if the permissible tensile stress is 35 N/mm. [Ans. 50 mm) 2. The maximum tension in the lower link of a Porter governor is 580 N and the maximum stress in the link is 30 Nimm. If the link is of circular cross-section, determine its diameter. (Ans. 5 mm) Тор Contents Simple Stresses in Machine Parts 117 3. A wrought iron rod is under a compressive load of 350 KN. If the permissible stress for the material is 52.5 Nimm, cakculate the diameter of the rod. JAns. 95 mm) 4. A load of 5 kN is to be raised by means of a steel wire. Find the minimum diameter required, if the stress in the wire is not to exceed 100 N/mm. (Ans. 8 mm) 5. A square tie bar 20 mm x 20 mm in section carries a load. It is attached to a bracket by means of 6 bolts. Calculate the diameter of the bolt if the maximum stress in the tie bar is…arrow_forward
- 2. Given: Two-dimensional truss structure as shown. (All joints are pin joints.) 65 lbs Fixed Point, Pin-Joint 9 in. 12 in. 60 lbs Material: Steel, diameter 1/2 in. Find: (a) Displacements of the nodes. (b) Normal stresses developed in the members. 45 lbs Fixed Point. Pin-Jointarrow_forwardPlease show intermediate steps including free body diagrams, equations used, problem setup etc. so that your approach can be followed Please do problem 1arrow_forward(1) E 4 kips C Lon -9 ft-9 ft——9 ft——94—- 1 kips What are the member forces in BD, BE and CE? Indicate if they are in tension (T) or compression (C).arrow_forward
- PLEASE ANSWER NUMBER 6.MECH 222-MECHANICS OF DEFORMABLE BODIES: PLEASE GIVE DETAILED SOLUTIONS AND CORRECT ANSWERS. I WILL REPORT TO BARTLEBY THOSE TUTORS WHO WILL GIVE INCORRECT ANSWERS.arrow_forwardHomework 3 m 13: Find the stresses in members BC, BD, and CF for the truss 3 m C 4 m hown in Fig. Indicate the tension or compression. The cross ectional area of each member is 1600 mm'. 60 kN 90 kN 4 m Figure P-113arrow_forwardplease see attached pic need force for memebers EG DG DFarrow_forward
- Please do it typed not handwriting. Make sure the answer is correct Don’t copy from any other online answers pleasearrow_forwardWrite application software program to find the shortest length of aluminium tubes 50 mm O.D. x 45 mm I.D. with minimum induced stresses to be used in a two-bar truss. The two tubes are hinged to supports that are 2 m apart, as illustrated below. Stress in the tubes should be kept below the yield strength of the material at 320 MPa. 2 m 200 Kgarrow_forwardPROBLEM 2 Given is a truss structure: Where: Working shear stress for the rivets is 70 MPa • Working bearing stress due to rivets is 140 Mpa Thickness of the member is 5 mm Thickness of the Gusset plate is 6 mm Rivet diameter is 15 mm Determine the no. of rivets to fasten the member BD 50 kN 30 kN B MATHalino.com 5 m 4 m 4 m 4 m 3 marrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY