
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
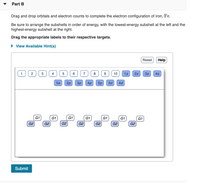
Transcribed Image Text:Part B
Drag and drop orbitals and electron counts to complete the electron configuration of iron, Fe.
Be sure to arrange the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the left and the
highest-energy subshell at the right.
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets.
• View Available Hint(s)
Reset
Help
4
6.
8
10
1s
2s
3s
4s
5s
2p
Зр
4p
5p
3d
4d
G1
G1
G1
G1
G1
G1
G1
G2
G2
G2
G2
G2
G2
G2
Submit

Transcribed Image Text:Part A
Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of phosphorus, P.
Be sure to label the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and
the highest-energy subshell at the top.
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Not all targets will be filled.
• View Available Hint(s)
Reset
Help
| 1
G2
G1
1s
G2
G1
G1 G1
2s
2p
G2
G1
3s
G2
G1
G1
G1
Зр
G2
G1
3d
G2
G1
4s
4p
1L
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Transcribed Image Text:W History Bookmarks Profiles Tab Window
sity and Sig x
eringchemistry.com/myct/itemView?assignment
late them to electron
cupation of orbitals by electrons
has two electrons in the 1s
ation of He is 1s².
writing the electron configuration
minimize the energy of
orbitals fill before higher-
following order:
5p 6s 4f 5d 6p 7s 5f 6d.
principle, orbitals can hold
and when two electrons
st have opposing spins.
-bitals of identical energy
Died singly with parallel
E
MasteringChemistry: Module 8 X
O
80
C
2
R
Q
F
V
%
5
T
Enter your payment details | ba X
ProblemID=201341795
G
11
2s
2p
3s
3p
3d
4s
Help
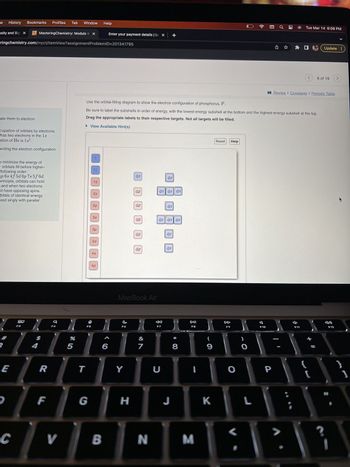
Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of phosphorus, P.
Be sure to label the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top.
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Not all targets will be filled.
View Available Hint(s)
4p
6
B
F6
G1
Y
G2
H
G2
G2
MacBook Air
G2
G2
&
N
G1
G1 G1 || G1
F7
+
G1
G1 G1 G1
G1
14EEBBBBBB
7
8
U
G1
J
DII
F8
I
M
(
9
Reset
K
Help
O
)
(Co
O
L
7
EX
F10
Ơ
Tue Mar 14 6:08 PM
P
* 0
Review I Constants I Periodic Table
+
Update:
6 of 19
{
[
F12
>
}
:
1
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question

Transcribed Image Text:W History Bookmarks Profiles Tab Window
sity and Sig x
eringchemistry.com/myct/itemView?assignment
late them to electron
cupation of orbitals by electrons
has two electrons in the 1s
ation of He is 1s².
writing the electron configuration
minimize the energy of
orbitals fill before higher-
following order:
5p 6s 4f 5d 6p 7s 5f 6d.
principle, orbitals can hold
and when two electrons
st have opposing spins.
-bitals of identical energy
Died singly with parallel
E
MasteringChemistry: Module 8 X
O
80
C
2
R
Q
F
V
%
5
T
Enter your payment details | ba X
ProblemID=201341795
G
11
2s
2p
3s
3p
3d
4s
Help
Use the orbital-filling diagram to show the electron configuration of phosphorus, P.
Be sure to label the subshells in order of energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the bottom and the highest-energy subshell at the top.
Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Not all targets will be filled.
View Available Hint(s)
4p
6
B
F6
G1
Y
G2
H
G2
G2
MacBook Air
G2
G2
&
N
G1
G1 G1 || G1
F7
+
G1
G1 G1 G1
G1
14EEBBBBBB
7
8
U
G1
J
DII
F8
I
M
(
9
Reset
K
Help
O
)
(Co
O
L
7
EX
F10
Ơ
Tue Mar 14 6:08 PM
P
* 0
Review I Constants I Periodic Table
+
Update:
6 of 19
{
[
F12
>
}
:
1
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- This energy diagram shows the allowed energy levels of an electron in a certain atom. (Note: the SI prefix 'zepto' means 10 can find the meaning of any SI prefix in the ALEKS Data tab.) -21 energy (zJ) 1400 1200 Continue USDJPY -0.55% 1000 800 600 400. 200 0 If the electron makes the transition shown by the red arrow, from A to C, calculate the wavelength of the photon that would be absorbed or emitted. Use this diagram to complete the table below. Round your answer to 3 significant digits. B -A Q Search 1 nm D x10 X Ś W DELL) You © 2023 McGraw Hill LLC. All Rights Reserved. Terms of Use | I CO Parrow_forwardGive correct detailed Solution with explanation needed..don't give Handwritten answer..give correct answerarrow_forward[References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. How many 5d orbitals are there in an atom? What is the maximum number of electrons possible in a set of 5d orbitals? Submit Answer Try Another Version 2 item attempts remaining Visited ot pt ptarrow_forward
- Question #4 on my review sheetarrow_forwardomework Questions: Quantum Theory, Atomic Structure, and Periodicity omework. Due in 26 minutes 9/15 answered HQ7.41 Homework • Unanswered Rank the following atoms from largest atomic radius (at top) to smallest atomic radius (at bottom). Drag and drop options into correct order and submit. For keyboard navigation... SHOW MORE V Sc Не Cs Sr Al 40 hulu II IIarrow_forwardNonearrow_forward
- How many orbitals in the n=5 engery level can have an ml value of 0?arrow_forward- Y tab Part A Enter the condensed electron configuration for Ni³+. Express your answer. condensed form in the order of orbital filling as a string without blank space between orbitals. For example, [He]2s22p² should be entered as [He] 2s^22p^2. ▼ Submit Request Answer aps lock Part B. Draw the orbital diagram for the ion Ni³+. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. Labels can be used once, more than once, or not at all. Targets may be left blank, such as for unused orbitals. Mother to Son &....pdf esc control COD ES ! 1 FI Q A N 2 1s 28 2p 3s 3p 3d 48 900 12 W S # # 3 X H 1 option command 80 F3 E D $ 4 C a R F 4p % 5 4 V 4d T 41 1 1L G MacBook Air ^ 6 Y B & 7 H F7 U N Reset Help * 8 J D-II FR I ( M 9 K O ) O I L d F10 - P command : ; FI t { + [ = 11 ? I option Show All F12 1arrow_forwardQuantum Numbers A. Quantum Numbers and Sublevels: Insert the appropriate values in the chart below. Principal Quantum # (n) 1 2 3 4 Possible Values for Angular Momentum Quantum # (/ 4 Letter Designation for each value of / Total Number of Sublevels per Level B. Quantum Numbers and Orbitals: Insert the appropriate values in the chart below. Principal Angular Momentum Quantum # (n) Quantum #(D) Possible Values for Magnetic Quantum # (m) Total Number of Orbitals per Sublevel C. Answer the following questions related to quantum numbers. 1. Indicate if the following sets of quantum number are valid. If invalid, circle the impossible value. a) n = 5,1 = 3, m/= -2, ms = -1/2 b) n = 2, 1 = 2, m/= 0, ms = + ½ c) n = 4, 1= -3, mi = 1, ms = + ½ d) n = 3, 1 = 0, mi= 0, ms = -½ e) n = 6, 1 = 1, mi = -1, ms = 1 f) n = 1, 1 = 0, m₁ = -2, ms = -½arrow_forward
- Review TConstants |PerIodic Tabie Learning Goal: To learn the restrictions on each quantum number. Part A Quantum numbers can be thought of as labels for an electron. Every electron in an atom has a unique set of four quantum numbers. What is the only possible value of m, for an electron in an s orbital? The principal quantum numbern corresponds to the shell in which the electron is located. Thus n can therefore be any integer. For example, an electron in the 2p subshell has a principal quantum number of n = 2 because 2p is in the second shell. Express your answer numerically. • View Available Hint(s) The azimuthal or angular momentum quantum number l corresponds to the subshell in which the electron is located. s subshells are coded as 0, p subshells as 1, d as 2, and fas 3. For example, an electron in the 2p subshell has l = 1. As a rule, l can have integer values ranging from 0 to n -1 Submit The magnetic quantum number mų corresponds to the orbital in which the electron is located.…arrow_forwardShow the orbital-filling diagram for N (nitrogen). Order subshells by energy, with the lowest-energy subshell at the left. Drag the appropriate labels to their respective targets. View Available Hint(s) Reset Help 1L 1 1s 2s 2p 3s Зр G1 G1 G1 G1 G1 G1 G1 G1 G1 G2 G2 G2 G2 G2arrow_forwardThe following sets of quantum numbers, listed in the order n, l, me, and ms, were written for the last electrons added to an atom. Identify which sets are valid and classify the others by the rule or principle that is violated. Drag the appropriate items to their respective bins. ►View Available Hint(s) Pauli violation 400+ 4 0 0 - 2 4 1 −1+1/2 4 1 0 + 21/1/2 + 4 1 +1 Other violation 1212 12 4 2 -1 + 420 4 2 +1 + 4 2 0 4 2 +2 + + + + + 12 12 12 3 1 -1 + 3 1 0 + 3 4+1+1/2 12 12 12 Valid Reset Helparrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY