
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
13th Edition
ISBN: 9780133923605
Author: Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
All three please
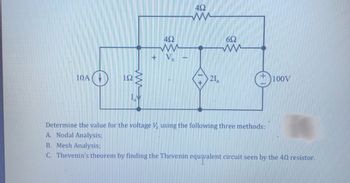
Transcribed Image Text:### Circuit Analysis Exercise
#### Problem Statement:
Determine the value for the voltage \( V_x \) using the following three methods:
1. **Nodal Analysis**
2. **Mesh Analysis**
3. **Thevenin's theorem** by finding the Thevenin equivalent circuit seen by the 4Ω resistor.
#### Circuit Description:
The given circuit features a combination of resistors, an independent current source, an independent voltage source, and a dependent current source. Refer to the circuit diagram below for component placement and connection:
- **Current Source**: 10A source
- **Voltage Source**: 100V source
- **Resistors**:
- A 1Ω resistor in series with the 10A current source
- Two 4Ω resistors in series-parallel configuration
- A 6Ω resistor in series with the 100V voltage source
- **Dependent Current Source**: \( 2I_a \), where \( I_a \) is the current flowing through the 1Ω resistor
#### Diagram Analysis:
- The `10A current source` is located at the extreme left of the circuit.
- The `1Ω resistor` lies in series to the 10A current source, placed just to its right.
- The `\(I_a\)` denotes the current through the `1Ω resistor`.
- A `4Ω resistor` is connected in series immediately to the right of the 1Ω resistor.
- The node where the series 4Ω connects also branches upward to another `4Ω resistor`, continuing rightward.
- The rightmost 4Ω resistor connects to a `6Ω resistor`.
- The `100V voltage source` is depicted at the extreme right of the diagram, in series with the 6Ω resistor.
- At the central node between the two 4Ω resistors lies the voltage \( V_x \).
- The dependent current source \( 2I_a \) connects the bottom node with the central node where \( V_x \) is located.
##### Analysis Methods:
**A. Nodal Analysis:**
- Use Kirchhoff’s current law (KCL) to determine the node voltages.
- Express the current through each resistor in terms of node voltages and solve the resulting system of equations.
**B. Mesh Analysis:**
- Apply Kirchhoff’s voltage law (KVL) to each independent loop.
- Define mesh currents, set up equations according to
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, electrical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Repeat above (insert image) with the resistors in parallel, insert multitesters (digital or analog) to measure current along each resistor. Comment on the meter readings and set up.arrow_forwardcan you do question iii please?arrow_forwardCan someone help with these worksheets and let me know if have any incorrect answers? Thank youarrow_forward
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON
Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780133923605Author:Robert L. BoylestadPublisher:PEARSON Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning
Delmar's Standard Textbook Of ElectricityElectrical EngineeringISBN:9781337900348Author:Stephen L. HermanPublisher:Cengage Learning Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Programmable Logic ControllersElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780073373843Author:Frank D. PetruzellaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Electric CircuitsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028229Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew SadikuPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON
Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)Electrical EngineeringISBN:9780134746968Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan RiedelPublisher:PEARSON Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,
Engineering ElectromagneticsElectrical EngineeringISBN:9780078028151Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,

Introductory Circuit Analysis (13th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780133923605
Author:Robert L. Boylestad
Publisher:PEARSON

Delmar's Standard Textbook Of Electricity
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9781337900348
Author:Stephen L. Herman
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Programmable Logic Controllers
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780073373843
Author:Frank D. Petruzella
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Fundamentals of Electric Circuits
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028229
Author:Charles K Alexander, Matthew Sadiku
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Electric Circuits. (11th Edition)
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780134746968
Author:James W. Nilsson, Susan Riedel
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Electromagnetics
Electrical Engineering
ISBN:9780078028151
Author:Hayt, William H. (william Hart), Jr, BUCK, John A.
Publisher:Mcgraw-hill Education,