
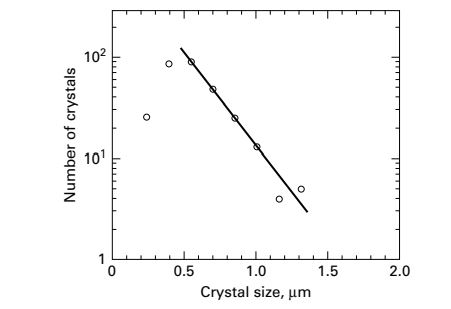
Tsuge and Matsuo studied precipitation of Mg(OH)2 by reacting aqueous solutions of MgCl2 and Ca(OH)2 in a 1-L MSMPR crystallizer operating at 450 rpm and 25oC. Crystal sizes were measured by a scanning-electron microscope (SEM) and analyzed by a digitizer. Crystal size was taken to be the maximum length. A plot of the crystal-size distribution is given in Figure for an assumed residence time of 5 minutes. Assuming that the number of crystals is proportional to exp(-L/Gτ), as in n=noexp(-L/Gτ), determine: (a) growth rate, (b) nucleation rate, and (c) predominant crystal size.
Magnesium hydroxide is precipitated by reacting of aqueous solution of MgCl2 and Ca(OH)2 in a 1-L MSMPR crystallizer.
The operating conditions of crystallizer are given as:
Temperature = 25 0C
Impeller speed = 450 rpm
The crystal size distribution is given in the figure.
Residence time = 5 min
Number of crystal is equal to,
n = n0e(-L/Gτ)
(a)
Growth rate of the crystal is calculated as follows:
The equation to calculate the number of crystal is given as,
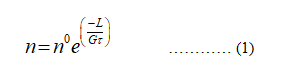
Where,
n represents the number of crystal.
n0 represents the proportionality constant.
L represents the length.
G represents the growth rate.
Ττ represents the residence time
The proportionality constant is also equal to,
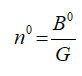
Where,
B0 represents the nucleation rate.
The equation (1) becomes,
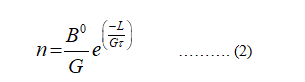
Take the log on the both sides of the equation (2)
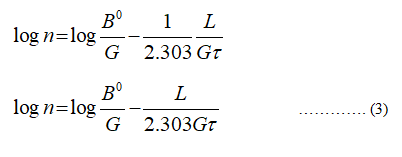
Equation (3) represents a straight equation (y = mx +c)
Where,
y = n
m= G/2.303τ
x = l
c = log B0/G
The values of unknowns are calculated as follows:
Take two values (extreme points) of number of crystals and corresponding values of the crystal size from the graph given in the question.
For n = 90
L = 0.6
For n = 3
L = 1.3
The residence time = 5 min
Plugin the values in equation (3)
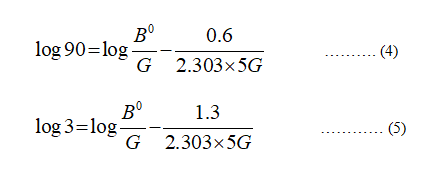
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps with 9 images

- In an air-carbon dioxide mixture at 298 K and 202.6 kPa, the concentration of CO2 at two planes (3 mm) apart are 15 vol% and 25 vol%. The diffusivity of CO2 in air at 298K and 202.6 kPa is 8.2x10-6 m2/s. Estimate the rate of transfer of CO2 across the two planes assuming: (i) Equimolar Counter diffusion (ii) Diffusion of CO2 through a stagnant air layer (iii) Compare the results of (i) and (ii) with valid justificationarrow_forwardSteelworks activities are important sources of fine particles, which may affect air quality in urban areas close to Fe-Mn-alloy manufacturing plants. In order to identify the identity of the particles, fine particles were sampled inside the chimneys of the plant. Explain briefly the surface analytical techniques in order to identify: (i) Particle composition. (ii) Particle size. (ii) Fe and Mn oxidation states in fine particles.arrow_forward50 g of pure Na2CO3 were dissolved in water and the volume of this solution was 200 mL. To this solution, 500 mL of 0.10 M HCl solution were added. Calculate the followings: Moles of Na2CO3 dissolved Moles of HCl added Moles of Na2CO3 reacted with HCl Moles of Na2CO3 left unreacted Molarity of Na2CO3 solution after the reactionarrow_forward
- The alkali metals (Li, Na and K) are promising energy storage materials usedin batteries. Lithium-ion batteries are found in almost all electronic devices encountered indaily life. The performance of these devices is constrained in part by the transport of alkalimetal ions in their electrolytes. Please calculate the diffusion coefficient of Li+, Na+ andK+ (with a Cl- counterion) by(a) treating them as ionic salts.arrow_forward1.6 Properties: Diffusivity Estimate the molecular diameter and diffusion coefficient for the proteins ribonuclease (MW 13,700 Da), hemoglobin (MW 68,000), and urease (MW 480,000), assuming the molecules are spherical and the density of each protein molecule is 1.3 g/cm³.arrow_forwardCompute diffusion coefficients for the interdiffusion of carbon in both (a) alpha-iron (BCC) and (b) gamma-iron (FCC) at 975 degrees C. Assume that D_0 for the interdiffusion of carbon in alpha-iron and gamma-iron are 1.1*10^-6 and 2.3*10^-5 m^2/s, respectively, and that Q_d are 80 and 148 kJ/mol, respectively.arrow_forward
- Consider an alloy that initially has a uniform carbon concentration of 0.20 wt% and isto be treated at 1000°C. The surface concentration is to be maintained at 1.30 wt% C.Calculate the carburizing time (in hour) necessary to achieve a carbon content of0.45 wt% at a position 2 mm into an iron–carbon alloy. The diffusion coefficient forcarbon in iron at this temperature is11 2 1.93 10 m sarrow_forwardFlash distillation is used to evaporate half of a 40 mole% methanol-water mixture. The pressure is 1 atm. a) What is the composition of the resulting distillate and residue? b) By changing the amount of evaporated mixture, what is the maximum possible methanol content of the distillate? c) By changing the amount of evaporated mixture, what is the maximum possible water content of the residue? Solve all problems (a-c) graphically.arrow_forward1) A biofilm is a layer-like aggregation of microscopic animals, plant or bacteria attached to a solid surface. Assume such a biofilm where the reactant is consumed Bulk fluid only at the solid surface, maintaining a particular value of surface concentration. Calculate the steady-state reactant flux into a biofilm of thickness 0.01 cm, if the diffusivity of the reactant in the biofilm is 0.8 cm²/day. Assume the reactant concentration in the bulk fluid to be uniform at 3.2 mg/liter. At the surface, reactant concentration is 0.25 mg/liter. Biofilm Surfacearrow_forward
- Using the following data, compare the effect of supersaturation ratio over the range of 1.005 to 1.02 on the primary homogeneous nucleation of AgNO3, NaNO3, and KNO3 from aqueous solutions at 25oC:arrow_forwardA binary gaseous mixture of components A and B at a pressure of 1 bar and temperature of 300 K undergoes steady-state equimolar counter diffusion along a 1-mm-thick diffusion path. At one end of the path the mole fraction of component A is 70%, while at the other end it is 20%. Under these conditions, DAB = 0.1 cm2/s. Calculate the molar flux of component A.arrow_forwardProvide basis, find, Process flow diagram and show step-by-step solution for the process. Topic: Material Balance with multiple units An aqueous solution containing 30mol% NaCl is used to produce NaOH by electrolysis. At the anode, the chloride ion is oxidized to chlorine gas; at the cathode, water is reduced to hydroxide and hydrogen gas. The chlorine gas and hydrogen gas exit the electrolysis system while the remaining solution is concentrated in an evaporator to produce a product containing 50mol% NaOH, 7mol% NaCl, and 43mol% H2O.a. What is the percent conversion of salt to sodium hydroxide?b. How much chlorine gas (in kg) is produced per kg of the product?c. How much water (in kg) must be evaporated in the evaporator per kg of the product?arrow_forward
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The





