
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
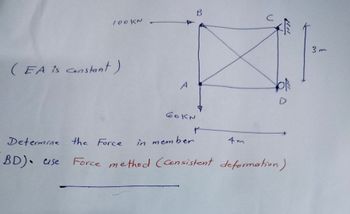
Transcribed Image Text:100kN
B
(EA is constant)
A
60KN
+
Determine the Force
in member
4m
D
BD) se Force method (Consistent deformation)
3 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- For the plane truss shown below loaded with a 200 kN force, determine the amount of deformation in membes (AB) & (AD) if their cross- sectional areas are known to be AB= 2500 mm² & AAD = 2000 mm² (assume E 200 GPa) 4 m B D 200 KN 2.5 marrow_forwardQuestion 5 Match the answers in the columns. v Maximum Shear stress of a cross section. A. using an l-section instead of a rectangular section. v Maximum Bending stress of a cross section. B. Tension and bending force. C. 1m form the supports - v If a simply supported beam is subjected to a distributed load, where are you most likely to find tension bending cracks. D. At Midspan - v Ifa simply supported beam is subjected to a distributed load, where are you most likely to find shear cracks. E. Midspan at the bottom v The bending stress in a section can be reduced by using a F. Midspan at the top v Shear stress can be increased by the width of a section. G. At the supports. v The shear force in fasteners. H. Reducing the width of a section. v Moment couple on a section. 1. using a rectangular section instead of an l-section J. Shear flow K. Increasing the width of a section. L. Only at the section sides touching the NA M. In between the NA and the top/bottom fibres N. Usually at the NA…arrow_forwardThe rods AB and CD are made of steel having a failure tensile stress of ?FAIL = 500MPa. Using a factor of safety F.S. = 2.0 for tension, determine their smallest diameter so that they can support the load shown. The beam is assumed to be pin connected at A and C. B A 1.5 kn/m 10m Figure 3.1 Suspended Floor Beam D Carrow_forward
- The rods AB and CD are made of steel having a failure tensile stress of ?FAIL = 500MPa. Using a factor of safety F.S. = 2.0 for tension, determine their smallest diameter so that they can support the load shown. The beam is assumed to be pin connected at A and C. B A 1.5 kn/m 10m Figure 3.1 Suspended Floor Beam D Carrow_forward0.15arrow_forwardReview: Design of simple structures 1. *1-96. Determine the required cross-sectional area of member BC and the diameter of the pins at A and B if the allowable normal stress is allow 3 ksi and the allowable shear stress is allow = 4 ksi. 1500 lb -2 ft -4 ft- 1500 lb B 60°arrow_forward
- For the truss loaded as shown, Determine the axial stress developed in members AB, AD, BC, and BD state what type of stress are developed. Considering that all members have the same cross- sectional area of 900mm^2.arrow_forwardSteel type is W310 X 74. P1= 40kN P2= 30kN. Find principal stress and shear stress at point '' a '' and '' b''arrow_forward15arrow_forward
- The rods AB and CD are made of steel having a failure tensile stress of ?FAIL = 500MPa. Using a factor of safety F.S. = 2.0 for tension, determine their smallest diameter so that they can support the load shown. The beam is assumed to be pin connected at A and C. B A 1.5 kn/m 10m Figure 3.1 Suspended Floor Beam D Carrow_forwardNEED ASAP. SOLVE CORRECTLY AND PROVIDE DETAILED SOLUTIONS. ALSO PROVIDE THE FBD PLEASEarrow_forwardThe truss is loaded by concentrated forces as shown in the figure. Use E = 30 x 106 psi and A = 0.90 in² for all the members. Determine the deformation sustained by members CG and FG. 12 kips 14 kips 16 kips A B с 10 kips |-6R-|-6A 8 ft ļE 5 ft ——6 ft—6 ft--6 ft-arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning